"Order pyridostigmine from india, muscle relaxant brand names."By: J. Matthew Brennan, MD - Associate Professor of Medicine
- Member in the Duke Clinical Research Institute
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/j-matthew-brennan-md
Generic pyridostigmine 60mg free shippingRequirements differ considerably from infant to infant and in the identical toddler over time; subsequently intakes must be individualized and frequently reassessed. Assessment of Fluid and Electrolyte Status Maternal situations throughout being pregnant, medication and fluids administered to the mom throughout labor and delivery, and particular fetal and neonatal circumstances all have an result on early fluid and electrolyte stability. Excessive administration of free water or oxytocin use within the mom may end up in hyponatremia in the neonate. Maternal therapy with indomethacin, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, furosemide, and aminoglycosides can all adversely affect neonatal renal perform. Serial measurements of physique weight, intake and output, and serum electrolytes will normally provide the most exact and correct info concerning overall fluid standing. Appropriate fluid stability within the first few days after start is related to a urine output of 1 to three mL/kg per hour and a weight lack of 5% to 10% in term infants and 10% to 15% in preterm infants. In critically ill infants and in situations of altered homeostasis, extra scientific knowledge that will assist in prognosis and administration include blood urea nitrogen, serum and urine osmolarity or specific gravity, urine electrolytes and serum bicarbonate, along with shut monitoring of blood stress and coronary heart rate. The frequency of monitoring is dependent upon the extent of immaturity and the severity of the fluid and electrolyte disturbance and of the underlying pathologic condition. Prostaglandins Prostaglandins have a well-documented, counterregulatory position for the renal vascular and tubular effects of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone and vasopressin (Bonvalet et al, 1987). The inhibition of those actions of prostaglandins by indomethacin ends in clinically important and typically detrimental renal vascular and tubular results in the preterm infant. The actions of prostaglandins modulating the consequences of the other regulatory hormones of neonatal fluid and electrolyte homeostasis are less well studied. Water Homeostasis and Management Water Losses Free water losses occurring through the pores and skin and the respiratory tract are thought-about insensible losses, whereas the smart water losses are composed of the amounts lost via urine and feces. Extremely preterm infants with out systemic hypotension or renal failure normally lose 30 to forty mL/kg/day of water within the urine on the first postnatal day and approximately 120 mL/ kg/day by the third day. High fetal plasma prolactin levels contribute to the elevated tissue water content of the fetus. Interestingly, postnatal prolactin ranges stay high within the preterm neonate till approximately the 40th postconceptional week (Perlman et al, 1978). Because of their renal immaturity, preterm neonates generally tend to produce dilute urine, thereby rising their obligatory free water losses. Normal water losses within the stool are less important, amounting to roughly 10 mL/kg/day in term infants and seven mL/kg/day in preterm infants in the course of the first postnatal week (Sedin, 1995). Water losses within the stool increase thereafter and are influenced by the type of feeding and the frequency of stooling. Although the skin matures quickly after birth, even in extremely immature infants, insensible losses are nonetheless somewhat larger at the end of the first month than within the time period counterparts. Among environmental factors, ambient humidity has the best impact on transepidermal water loss. In extremely immature neonates, a rise within the ambient humidity of the incubator from 20% to 80% decreases the transepidermal water loss by approximately 75% (Sedin, 1995). However, the use of an open radiant hotter greater than doubles transepidermal water losses (Flenady and Woodgate, 2003). Applying a plastic heat shield while the toddler is underneath the hotter can decrease transepidermal water loss by 30% to 50% (Costarino et al, 1992). At low ambient humidity, phototherapy will increase transepidermal water losses by approximately 30%. On the opposite hand, halogen highlight phototherapy increases transepidermal water loss in premature infants by 20% despite fixed skin temperature and relative humidity (Grunhagen et al, 2002). Insensible water losses from the respiratory tract rely primarily on the temperature and humidity of the inspired gasoline combination and on the respiratory price, tidal quantity, and lifeless area ventilation. However, in infants undergoing mechanical air flow there will be no insensible losses by way of the respiratory tract if the ventilator gas mixture is humidified at physique temperature. The most commonly encountered extraordinary water losses happen when a nasogastric tube is positioned underneath steady suction (to be discussed later on this chapter). Large losses can also happen in association with chest tubes, different drains, ostomies, and fistulas as nicely as with emesis or diarrhea. Management of Water Requirements Appropriate administration requires estimating any existing deficits or surpluses, calculating ongoing maintenance needs due to ordinary wise and insensible losses and development and additional wants on account of extraordinary losses. The most helpful parameter for monitoring fluid steadiness is the load of the infant, as rapid adjustments in weight will mirror adjustments in water steadiness. These numbers are tips for initial administration only; the strategy must subsequently be individualized based mostly on laboratory values and different medical data. Serum sodium ranges ought to be measured every four to eight hours untilstabilized, normally by three to four days after delivery, and urine output ought to be recorded and reviewed every 6 to 8 hours. Once knowledge are available, fluids must be increased if weight loss is bigger than 1% to 2% per day in term infants and 2% to 3% per day in preterm infants, if urine output is low, if urine particular gravity is rising, or if serum sodium concentration is rising. Overall, expected and appropriate weight reduction in the first week of life is as much as 10% in time period infants and as a lot as 20% in preterm infants. The aim is to attain one hundred forty to one hundred sixty mL/kg/day of fluids by 7 to 10 days to permit for enough caloric consumption. Overhydration can generally be prevented by the use of blood transfusions or dopamine as an alternative of colloid or crystalloid, if appropriate, for blood pressure help. In addition to reducing the necessity for quantity boluses, dopamine may facilitate the method of extracellular quantity contraction via its renal and hormonal effects (Seri, 1995). The complete water deficit may be estimated by utilizing weight modifications, calculating complete inputs and outputs, and following serial sodium ranges. Free water deficit (or excess) could be calculated as: H2 O deficit (or excess) (L) = [0. When dehydration is diagnosed, correction should typically occur over 24 hours, with half correction over eight hours and the rest over the next sixteen hours. Longer correction occasions are indicated when dehydration is accompanied by moderate to extreme hypernatremia. Treatment is finest approached by contemplating individually the fluid resuscitation requirements, fluid to substitute present deficits and ongoing losses, and upkeep necessities, because the quantity of the fluid, the composition, and the rate of substitute differ for each. Resuscitation of the intravascular volume to restore blood pressure and perfusion ought to be supplied with boluses of isotonic saline (0. The remaining deficit substitute quantity must be with fluid of acceptable sodium content material based mostly on the serum sodium (see Sodium and Potassium Homeostasis and Management, later), usually zero. Extraordinary losses brought on by tubes, drains, emesis, diarrhea, and ostomies should always be sought in the dehydrated toddler and also accounted for in fluid administration. The composition of this latter substitute resolution is dependent upon the electrolyte concentration of the fluid loss. The commonest extraordinary loss, gastric fluid, accommodates vital sodium and chloride. For extra particulars of fluid correction and sodium management, see the dialogue beneath Management of Hypernatremia later on this chapter.
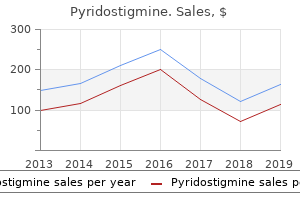
Order pyridostigmine cheap onlineNumerous trials (Duley et al, 2001) have been conducted with lowdose aspirin, primarily based on the concept that the ability of aspirin to irreversibly inhibit production of the vasoconstrictive prostaglandin thromboxane would promote higher exercise of prostacyclin, a vasodilatory prostaglandin. This capability of aspirin would assist to keep patency within the maternal placental vascular bed and limit or stop the evolution of preeclampsia. Unfortunately, although a modest discount within the frequency of preeclampsia (approximately 15%) was documented, no improvement in key measures of perinatal consequence was demonstrable in a metaanalysis of the outcomes of obtainable research (Duley et al, 2001). Calcium supplementation was briefly in vogue as a preventive remedy within the Nineteen Nineties, on the idea of the known vasodilatory impact of calcium and spectacular results in earlier, small research (Atallah et al, 2000); nevertheless, its value was not supported in a metaanalysis (Atallah et al, 2000). Of concern was the discovering that ladies in whom preeclampsia developed regardless of vitamin therapy had markedly worsened preeclampsia than controls in whom the illness developed. Antepartum Management Given the current inability to predict or stop preeclampsia, clinicians are left to address established disease and to attempt to prevent maternal and fetal morbidity. The division of established preeclampsia into delicate and extra extreme types is of great price in figuring out administration and minimizing morbidity (see Box 11-1). The look of extreme preeclampsia mandates supply in all but highly selected instances regardless of gestational age. Patients with a prognosis of gentle preeclampsia ought to be evaluated for signs of maternal or fetal compromise, which would make their disease severe. Evaluation ought to embrace a 24-hour urine collection to consider for proteinuria; full blood count and platelet measurements; determination of serum uric acid, blood urea nitrogen, and creatinine ranges; and analysis of liver transaminases. Patients at earlier gestational phases ought to be closely monitored with sequential scientific and laboratory evaluations. Such monitoring often begins within the hospital and may be continued in an outpatient or home setting with applicable supervision. If the medical picture deteriorates or time period is reached, the infant should be delivered. Fetal well-being should be evaluated until delivery via kick counts and common non-stress exams or modified biophysical profiles. Such sufferers could additionally be managed conservatively beneath shut supervision while antenatal corticosteroids are administered with out adversely affecting maternal or fetal outcome (Sibai et al, 1990). Severe hypertension requires remedy with fast-acting antihypertensive brokers if stroke and placental abruption are to be avoided. The purpose of remedy is to decrease blood strain into the gentle preeclampsia vary (140/90 mm Hg) to scale back the risk of stroke and other maternal cardiovascular problems. There is proof to support the use of parenteral magnesium sulfate to stop eclampsia in all circumstances of extreme disease (Duley et al, 2003). Severe preeclampsia can manifest as basic disease with extreme proteinuric hypertension, or it can trigger atypical findings similar to pulmonary edema or extreme central nervous system signs, together with blindness. Earlier reviews advised that the illness carries a grave prognosis (Weinstein, 1982). Many sufferers are able to ship vaginally, however fetal compromise might preclude aggressive induction and mandate supply by cesarean section. Nonetheless, the morbidity of such infants is larger because of hypoxemic insults received in utero. Infants born to mothers with preeclampsia can also have thrombocytopenia or neutropenia, which additional complicates their newborn course (Fraser and Tudehope, 1996). Although the absolute threat of seizure is low (1 in 2000 to 3000), the occurrence of seizures is unpredictable, and the efficacy of magnesium sulfate and margin of safety has been validated in a quantity of randomized trials (Duley et al, 2003). Blood pressure must be maintained within the mild preeclampsia vary using intravenous antihypertensive brokers (labetalol, hydralazine). Epidural anesthesia is indicated for ache management and to help in blood stress management. There is a substantial drop within the risk of eclampsia by forty eight hours postpartum, with seizures occurring in lower than 3% of women beyond that time. Most sufferers have antecedent features which may be suggestive of preeclampsia, although in some cases eclampsia might happen with out warning. If eclampsia is left untreated, repetitive seizures turn into more frequent and of longer period, and in the end standing eclampticus develops. Maternal and fetal mortality could additionally be as excessive as 50% in severe cases, particularly if the seizures happen while the patient is far from medical care. Randomized controlled trials have demonstrated the clear superiority of magnesium sulfate for the remedy of eclampsia over all other anticonvulsants (Duley and Gulmezoglu, 2002; Duley and Henderson-Smart, 2002b, 2002c). Intravenous magnesium sulfate is given as a 4-g bolus over 5 minutes followed by a upkeep infusion of 1 to 2 g/hr for twenty-four hours after supply. In refractory cases, second-line therapy with other anticonvulsants may be required, or the patient may should be paralyzed and their lungs ventilated. Delivery after an eclamptic seizure should happen in a controlled, cautious method. There is little to be added by performing an emergency cesarean part (Coppage and Polzin, 2002). Vaginal delivery is feasible typically, though cesarean delivery could additionally be indicated if the status of the cervix is unfavorable or if fetal compromise is ongoing despite management of seizures and maternal stabilization. It affects roughly 1 in 2500 deliveries within the United States and could also be much more frequent in growing international locations, affecting as many as 1% of parturients. Gleason Substance abuse during pregnancy has been recognized as a problem for more than a century. Psychotropic substances, each legal (alcohol, cigarettes, and pharmaceuticals similar to opioids and benzodiazepines) and unlawful (opioids, amphetamines, cocaine, and marijuana), may cause obstetric, fetal, and neonatal complications. These issues embody poor intrauterine development, prematurity, abruptio placenta, fetal distress, spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, fetal (and maternal) cerebral infarctions and different vascular accidents, malformations, and neonatal neurobehavioral dysfunction. Although substance abuse happens in all socioeconomic lessons, illegal drug abuse is more regularly related to unhealthy lifestyles, poor entry to prenatal care, untreated health issues, poverty, stress, and psychological disorders. This chapter addresses the epidemiology of perinatal substance use and abuse; the consequences of particular medicine on the fetus and newborn; maternal points and their effects on the new child; identification of pregnancies and infants at risk; neonatal administration; and long-term results and follow-up. The dialogue will concentrate on abused substances which are known or instructed to be related to important perinatal and neonatal morbidity: alcohol, tobacco, nicotine, opioids, cocaine, marijuana, and methamphetamine. One of essentially the most comprehensive geographically based prevalence studies on substance use and abuse by pregnant ladies was undertaken in California in the early Nineties by the Perinatal Substance Exposure Study Group (Vega et al, 1993). In that study, urine was collected on the time of delivery from more than 30,000 pregnant women. The authors concluded that if these outcomes could presumably be extrapolated to the United States at massive, an estimated 450,000 infants per yr (11% of four million reside births) can be exposed to alcohol, illicit medicine, or each in the days before supply. Department of Health and Human Services Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System is designed to monitor maternal behaviors and experiences amongst girls who deliver live-born infants. Data collected throughout 2000 to 2003 from 19 states revealed that over the last three months of pregnancy, tobacco use ranged from four. Data from a 2005-2006 National Survey on Drug Use and Health revealed that of pregnant ladies aged 15 to forty four, 4% reported utilizing illicit medication, 16.
Order pyridostigmine from indiaThe resulting congenital diaphragmatic hernia leads to pulmonary hypoplasia of the lung ipsilateral to the diaphragmatic defect as bowel and strong viscera migrate into the thorax. Pulmonary hypoplasia can also prolong to the contralateral lung as the mediastinum shifts due to accumulating belly viscera within the thorax. Lung improvement can be organized into stages (embryonic, pseudoglandular, canalicular, saccular, and alveolar), although the timing of these phases is considerably imprecise and appreciable overlap can happen. The canalicular phase is marked by completion of the conducting airways by way of the level of the terminal bronchioles, and the development of the rudimentary fuel trade units that are not invested with cartilaginous assist. The acinus is the gasoline change unit of the lung and encompasses a respiratory bronchiole and all of its associated alveolar ducts and alveoli. A terminal bronchiole with all its related acinar constructions constitutes a lobule. Branching of those distal airspaces continues on a extra restricted foundation in the course of the canalicular phase, lastly achieving a complete of 23 airway subdivisions. Beyond this point, the effectivity of gasoline exchange is determined by the available surface space. Lengthening and widening of the terminal sacs expands the fuel trade surface area. Each saccule consists of smooth-walled airspaces with thickened interstitial areas containing a double capillary community. These will give rise to two to three alveolar ducts, further expanding the available floor space. Postnatal lung development may be subdivided into extra stages (Burri, 2006). The improvement of major alveoli is followed by an extra expansion of the gas-exchange surface space via the formation of septae or secondary crests (see Alveolarization, later). An initial section of bulk alveolarization happens inside the first 6 months postnatally, with a more modest addition of secondary alveoli by way of the rest of this period. These immature secondary alveoli include a double capillary bed, whereas adult alveoli are invested by a single capillary mattress. Microvascular maturation, the subsequent part of postnatal lung development, occurs between the first few postnatal months of life by way of three years of age (see Development of the Pulmonary Vasculature, later). Estimates have ranged from as early as 2 years to as late as 20 years old in humans; this is further complicated by the observation that alveolar expansion can happen in response to pneumonectomy in grownup animals and humans. The acquisition of alveoli after the maturation of the microvasculature has been termed late alveolarization. This exercise has been most often demonstrated in subpleural areas of the lung and likely invokes mechanisms just like secondary crest formation. While alveolarization wanes over the first three years of life in the human, growth of the lung continues to broaden the fuel exchange surface. Between 2 years of age and adulthood, lung tissue expands with lung quantity roughly proportionately to the rise in bodyweight of the child. The extent to which these developmental mechanisms could be harnessed after untimely birth, with or without superimposed lung damage, is a topic of lively investigation. Differentiation proceeds in a centrifugal style from proximal to distal airspaces, lagging behind branching. Temporal and contextual alerts foster the regionalization of epithelial cell varieties. Proximal Airways the airway epithelium is tall and columnar, reducing to a extra cuboidal appearance more distally (Jeffrey, 1998; Snyder et al, 2009). The endodermal epithelial lining cells of the trachea and bronchi partition into four cell varieties: undifferentiated columnar, ciliated, secretory-goblet, and basal cells. The variety of mucin-producing goblet cells in airways peaks at mid-gestation in the fetus and declines into adulthood. Basal cells have a crucial role in regenerating injured massive airway epithelium (see Stem and Progenitor Cells within the Lung, later). Submucosal glands are found in the interstitium between the cartilaginous tissue and surface epithelium, and so they have a significant position in airway host defense. Submucosal gland improvement could be characterized by five levels: (1) epithelial budding and invasion of the lamina propria, (2) improvement of a lumen, (3) initiation of tube branching, (4) dichotomous branching, and (5) repeated dichotomous branching. By comparison, the airways of infants and youngsters include comparatively extra submucous glands than do adults. The glands are lined by mucous cells proximally and serous cells extra distally, the latter comprising 60% of the entire epithelial cell content of the glands. Serous cells secrete water, electrolytes, and proteins with antimicrobial, antiinflammatory, and antioxidant properties, whereas the mucous cells produce primarily mucins. In addition to this host defense function, submucosal glands also include a population of basal cells that respond to injury of the airway by replenishing the airway epithelium. Muscular investment of the airways begins as early as 6 to eight weeks gestation as smooth muscle cells are identifiable around the trachea and large airways. Fetal airway clean muscle is innervated and in a position to contract through the first trimester. An further airway cell deserves point out due to its role in all kinds of pediatric illnesses. Although they arise from foregut endoderm, the cell of origin is distinct from different epithelial elements of the lung. Distal Airways the bronchiolar epithelium differs from the more proximal airway epithelium. In addition to being extra cuboid in look, the epithelium contains progressively fewer ciliated cells and goblet cells, which are in the end absent from the terminal bronchioles. Instead, the nonciliated, secretory Clara cell is found in rising numbers and density down the conducting airways, such that the Clara cell is probably the most abundant cell of the terminal bronchiole (Jeffrey, 1998). Clara cells are critical to the host protection and detoxification features of the lung. This specialized cell produces the best levels of cytochrome P-450 and flavin monooxygenases within the lung. While critically essential in detoxing, these enzymes take part within the bioactivation of procarcinogens as nicely, inserting the Clara cell in a precarious position as a major goal of poisonous metabolites. The Clara cell also has an important role in immunoregulation in the distal airways. The secretion of antiproteases from Clara cells suggests that they modulate the protease-antiprotease steadiness in the distal lung. Alveolar Epithelium During the 4th through 6th months of gestation, the epithelial cells lining the acini start to differentiate additional (Mallampalli et al, 1997). The cuboidal epithelial cells accumulate giant glycogen shops and develop small vesicles containing free lamellae. The massive glycogen pools provide a prepared source of substrate required for the production of accelerating amounts of surfactant phospholipids, they usually lower in dimension as surfactant manufacturing advances within the fetal lung. In cells destined to turn into kind 2 cells, lamellar bodies become bigger, extra numerous, and more densely filled with surfactant phospholipids and proteins, whereas these cells destined to become sort 1 cells, upon dropping their relationship to mesenchymal fibroblasts, lose the prelamellar vesicles and become progressively thinner, thereby adopting a phenotype extra suitable for gasoline exchange. Alveolar type 1 and a couple of cells are readily identified early in the saccular stage of fetal lung growth. There is rising appreciation for the alveolar sort 1 cell as more than a passive membrane for gasoline trade (Williams, 2003).
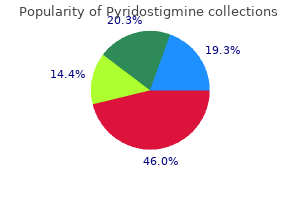
Buy pyridostigmine with a visaDelayed lactogenesis occurs in 20% to 30% of mothers; however, in most cases the primary drawback is related to toddler breastfeeding behaviors in the first few days of life. Studies on breastfed neonates point out that approximately 10% of infants lose more than 10% of their birthweight in the course of the first few days of life (Dewey et al, 2003). Mothers with previous breast surgery, significantly breast reduction, are at elevated threat of major insufficient lactation. Prolonged labor and cesarean supply have been associated with delayed onset of milk manufacturing (Dewey et al, 2003). The adequacy of breastfeeding behaviors may be assessed through the newborn nursery keep utilizing scoring methods such as the Infant Breastfeeding Assessment Tool. Low scores on this measure through the first day of life are reasonably predictive of excessive weight reduction in the neonate (Dewey et al, 2003). Decreased numbers of voids and stools in the new child are also helpful in figuring out youngsters with breastfeeding problems, but this information is most helpful after day 3 of life. Despite this discovering, transmission of infection via breastfeeding has not been documented. There are three main classes of formula used in neonates: cow milk�based, soy, and hydrolyzed formula. Because the primary carbohydrate in soy formulation is sucrose or corn syrup, soy formulation can be used in neonates with potential galactosemia. These formulas are presupposed to lead to fewer allergies in babies and youngsters than does cow milk�based formulation, however the proof for this is limited (Osborn and Sinn, 2006). Standard preparations of formulation available for use in healthy time period neonates provide zero. Most formulas are fortified with 10 to 12 mg/L of iron; nevertheless, some low-iron cow milk�based formulation are available. It is recommended that each one formula-fed newborns obtain the iron-fortified products. Mothers who elect to bottle-feed report feeling unsupported for their decision by well being care professionals, and as a lot as 50% feel pressured to breastfeed (Lakshman et al, 2009). It can additionally be important to provide practical education about bottle-feeding to these parents; this is regularly neglected in many newborn nurseries (Lakshman et al, 2009). Average formulation consumption in time period newborns during the first day of life is 15 to 20 mL/kg and 40 to 45 mL/kg in the course of the second day. Supplementation of Breastfeeding It is usually pointless to provide any vitamin or fluid to full-term breastfed infants beyond human milk. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are commonly used to deal with despair and anxiousness in young women. Among medicine in this category, sertraline and paroxetine are thought to be the safest to be used in breastfeeding mothers, whereas fluoxetine and citalopram are believed to have probably the most potential for toxicity in the neonate (Field, 2008). Overall there have been few antagonistic results noted with use of any of these medicine, and usually the potential dangers associated with these medicines are thought to be outweighed by the advantages of breastfeeding (Field, 2008). Parents showing regarding behaviors, probably resulting in abuse or neglect, ought to have supervision and interventions to help them, presumably leading to termination of parental rights (Davidson-Arad et al, 2003; Wattenberg et al, 2001). There are a number of major challenges for fogeys of normal newborns: sleep deprivation, studying to calm a crying infant, significant life adjustments, and the new worries that include being liable for a totally dependent being. Postpartum melancholy is more common and of longer duration than beforehand thought, and it occurs in at least 10% of moms. This condition is said to sleep deprivation and has major and long-lasting results on toddler homeostasis and improvement (Chaudron, 2003). Anticipatory steering must be given to help prepare new dad and mom for the common tasks of newborn care and to educate them concerning the many regular variations in new child habits. Most parents have questions about feeding, elimination, bathing, wire care, genital care, jaundice, and common rashes. There are quite a few checklists of educational matters that can be overwhelming to new dad and mom. In addition, learning types can vary, with some preferring written supplies and whereas others preferring audio-visual materials or hands-on demonstration. Ideally, schooling ought to be focused towards the matters of interest and with the appropriate materials for learning style (Dusing et al, 2008). Mothers are often not in an excellent studying state in the instant postpartum interval because of pain, postpartum hormonal changes, and the stress of being in a hospital. There is a few evidence that providing parental education utilizing tools corresponding to interactive video and computers may be superior to conventional instructing (Snowdon et al, 2009; Trepka et al, 2008). There can also be a philosophical choice in deciding whether to emphasize the overall well being of a new child or to concentrate on prevention or identification of illness. There is little proof for the efficacy of most anticipatory guidance offered to mother and father through the new child nursery keep. A notable exception is the recommendation to put infants to sleep in the supine position (described within the following section). There can also be rising proof that training concerning the normality of inconsolable crying in infants helps dad and mom deal with this stressful situation, and it could scale back the risk of shaken baby syndrome (Barr et al, 2009). Sleep Position With the exception of immunizations, no youngster well being intervention up to now 20 years has resulted in a bigger lower in postneonatal toddler mortality than the "Back to Sleep" campaign. A multipronged effort together with brochures, public service bulletins, and schooling offered by well being care professionals was used to affect the change in sleep place (Willinger et al, 2000). Obviously schooling offered to dad and mom during the newborn nursery keep is a crucial determinant of the sleep place of an infant. It is really helpful that infants sleep on agency surfaces and without extreme bedding such as pillows. Many consultants also suggest in opposition to co-sleeping between dad and mom and infants; however, this subject is controversial and the evidence is somewhat contradictory. Because approximately 50% of infants born by vaginal delivery are discharged earlier than the age of 48 hours, and because as much as 40% of these born by cesarean delivery are discharged before 72 hours of age, a large proportion of neonates are discharged before the age of 3 to four days, when bilirubin ranges sometimes peak and breastfeeding is well established (Paul et al, 2006). This follow-up can be accomplished both by a go to to a health care provider or via a home nursing go to. Consideration of a longer nursery stay is usually recommended for infants with a number of of these threat components. The reason for delayed voiding is likely a consequence of stress on the toddler during labor and delivery (Vuohelainen et al, 2007; 2008), which is a protecting mechanism for the infant. Normally no intervention is needed once homeostatic adaption to extrauterine life is steady. The differential prognosis of delayed voiding (defined as no urine output by 24 to forty eight hours of age) consists of renal and postrenal causes. Most infants with bilateral renal agenesis have other findings, similar to oligohydramnios or Potter sequence.
Buy pyridostigmine paypalThe gag reflex must be examined if the infant is neurologically depressed or has problem swallowing. The whole skin surface of the neck ought to be visualized and palpated, whereas turning the top and retracting the skin to open the neck creases and folds. Congenital muscular torticollis at start is often but not invariably accompanied by a palpable fibrous tumor (fibromatosis colli) in the shortened sternocleidomastoid muscle. Nonmuscular causes of torticollis embrace tumors of the posterior fossa or cervical backbone and malformations of the cervical backbone. A quick neck, low hairline at the back of the top, and restricted mobility of the upper spine are characteristic options of the Klippel-Feil syndrome. Redundant skin or a webbed neck may be seen in Trisomy 21 and in Turner and Noonan syndromes. Cystic hygromas are gentle, fluctuant lots that transilluminate and are usually unilateral. Branchial cleft cysts or sinuses are also found laterally, from the level of the mastoid to the middle of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Thyroglossal duct cysts are situated in the midline excessive in the neck or beneath the chin. Further investigation is required if the larynx or trachea are displaced from the midline, or if enlargement of the thyroid gland is suspected. The position of the nipples and the presence of any accent nipples must be famous. The definition and stippling of the areola and the size of the breast bud are developmental options helpful as a half of scoring for gestational age estimation. Transient galactorrhea occurs in roughly 5% of term neonates (Madlon-Kay, 1986). Variations in the form of the xiphoid course of are widespread, and oldsters can be reassured that a outstanding or bifid xiphoid is benign and will usually turn out to be a lot much less obvious because the toddler grows. A mildly depressed sternum (pectus excavatum) or protuberant one (pectus carinatum) is often of no scientific consequence. A small, bell-shaped chest in an toddler with respiratory misery could mirror lung hypoplasia or a disorder of skeletal development. An improve in the anterior-posterior diameter of the chest (barrel chest) might replicate a rise in the intrathoracic quantity caused by air trapping from meconium aspiration or pneumothorax. Palpation of the chest wall may reveal irregularities or tenderness, and crepitus may be felt at the web site of a fractured clavicle or rib. Crepitus may also be attributable to dissection of air into the subcutaneous tissue from a pneumothorax or pneumomediastinum, but this is an unlikely occurrence in an asymptomatic infant. In the conventional new child, the stomach expands easily with every contraction of the diaphragm, whereas the chest moves inward slightly. The respiratory fee of the newborn infant is highly variable when the toddler is awake, changing with exercise similar to feeding and crying. Tachypnea during sleep is extra clearly associated with respiratory problems than is tachypnea throughout awake states. Because short pauses and brief intervals of rapid respiration are widespread in normal newborns, correct measurement of the respiratory fee requires counting for a full minute, ideally when the infant is asleep or at least not crying. During crying, the standard and vigor of vocalization are assessed, and the infant is noticed for modifications in color and perfusion. Central cyanosis that solely seems during crying may be brought on by cardiac or respiratory illness and requires further evaluation. Cyanosis that resolves throughout crying could additionally be because of choanal atresia or stenosis, apnea, or hypoventilation. The traditional symptoms of respiratory distress are nasal flaring, grunting, and retractions. Nasal flaring and gentle grunting are frequent within the quick postnatal period, however within the wholesome new child they should resolve inside 15 to 20 minutes after birth. Increasing respiratory distress brought on by decreasing lung compliance is usually mirrored in a progression from nasal flaring, or delicate tachypnea, or each; to nasal flaring plus gentle or intermittent grunting; and then to flaring, grunting, and increasingly extreme retractions. The respiratory fee typically decreases because the work or effort of breathing will increase, as indicated by the event of grunting and increasing retractions. When respiratory distress is mild, intermittent grunting at a slower respiratory rate could alternate with durations of mild tachypnea. As grunting becomes extra extreme, the expiratory part becomes increasingly extended. The length of the grunt, somewhat than its loudness, correlates with the severity of distress. The rhythm of grunting and its incidence on the finish of expiration are key options that help to distinguish it from different vocalizations. Retractions require a forceful inspiratory effort and decreased lung compliance, they usually could also be absent or much less prominent than anticipated in an infant with neuromuscular melancholy. Nasal congestion, airway obstruction, and airway secretions can produce sounds which would possibly be audible without a stethoscope. Noisy or congested nasal respiration and intermittent sneezing not related to higher respiratory an infection is frequent within the first few days after start. Because intubation of vigorous infants born by way of meconiumstained amniotic fluid is not routine (Halliday and Sweet, 2001), hoarseness or stridor brought on by vocal cord trauma in wholesome term infants is less frequent than beforehand. Inspiratory stridor is because of narrowing or partial obstruction of the upper airway. The presence and loudness of the stridor is dependent upon respiratory effort in addition to the extent of airway narrowing, so that stridor worsens with forceful inspiration throughout crying. Detection of abnormal lung sounds together with crackles, wheezes, and rhonchi requires further evaluation. If more detailed examination is indicated, auscultate over the 4 main quadrants anteriorly, on the perimeters, and on the upper and lower back bilaterally. Diaphragmatic hernia manifesting in the neonatal period usually causes important respiratory misery, but rarely a small diaphragmatic hernia is detected by the presence of bowel sounds within the chest in an asymptomatic infant. Spontaneous cough, which is abnormal in neonates, is mostly brought on by infection or aspiration. Percussion of the chest, rarely accomplished as a part of routine examination of newborn, can be helpful for estimating the position of the higher margin of the liver. Percussion can be used to detect a large effusion or lung consolidation, but infants with these circumstances could have other symptoms of respiratory distress, so the analysis will rely on imaging studies and never the bodily examination. Respiratory signs are delicate however nonspecific indicators of sickness within the new child, because alterations in respiration (including apnea) can accompany illness of many various etiologies. Common causes of delicate or mild respiratory distress detected in the routine evaluation embody retained fetal lung fluid (transient tachypnea of the newborn), spontaneous pneumothorax, neonatal sepsis, pneumonia, meconium or amniotic fluid aspiration, and congenital coronary heart illness. Although detection of coronary heart illness is important, irregular circulatory findings in the newborn are more often secondary to other problems, together with sepsis, hypovolemia, anemia, and hypoglycemia. The cardiovascular system undergoes marked changes after start involving the transition to air respiration, the progressive decrease of pulmonary vascular resistance, and the closure of the ductus arteriosus. These changes have an effect on the bodily examination of healthy infants and people with congenital coronary heart disease; subsequently the time after birth is all the time an necessary consideration within the interpretation of the examination. These features will often be inspected at completely different occasions in the course of the course of the routine examination, however they need to be reevaluated in the course of the heart and chest examination if cardiovascular abnormalities are suspected.
Syndromes - Name of the product (ingredients and strength, if known)
- Do you use a soft- or hard-bristle toothbrush?
- You may be asked not to drink or eat anything 6-12 hours before your procedure.
- Difficulty waking up or becoming more sleepy
- Staples, screws, or plates may be used, depending on the type of osteotomy.
- Medicines to treat infections and clotting disorders
- Noncancerous mouth sores (the specific cause can be determined in many cases)
- Breathing support
- Fainting or feeling light-headed
- If you smoke, try to stop. Ask your doctor or nurse for help.
Generic pyridostigmine 60 mg overnight deliveryA Dutch study compared the outcomes of triplets delivered vaginally and abdominally at two institutions (Learman, 1998). One hospital favored cesarean section, whereas at one other trial of labor was offered to all applicable candidates. Vintzileos et al (2005) tried to estimate the dangers of stillbirth and neonatal and infant deaths in triplets, in accordance with mode of delivery; they used the "matched multiple delivery" data file that was composed of triple births that had been delivered in the United States during 1995 via 1998 and located that 95% of all triplets had been delivered by cesarean delivery. Vaginal delivery (all vaginal) was associated with an increased threat for stillbirth (relative danger, 5. They concluded that cesarean supply of all three triplet fetuses is related to the bottom neonatal and infant mortality price and that vaginal supply among triplet gestations ought to be avoided (Vintzileos et al, 2005). Thus delivery of triplet gestations vaginally while not an unreasonable strategy has almost disappeared from the practice of contemporary obstetrics in favor of routine cesarean delivery. Currently quadruplets and different higher-order multiples are often delivered by cesarean section (Ron-El et al, 1981). Surgery carries the maternal risks of increased blood loss, extended hospital keep, and longer restoration period in contrast with vaginal supply. During the 1980s to Nineteen Nineties, efforts were made to encourage ladies to try vaginal birth after a prior cesarean delivery, because success rates vary from 60% to 80% for vaginal supply, dependent on the indications for the prior cesarean supply (Benedetto et al, 2007). This lower has significantly affected the United States cesarean section price of 31. A recent giant, retrospective research evaluated 20,095 girls with a historical past of prior cesarean supply and located that rupture risk was 0. Most just lately, Kamath et al (2009) performed a retrospective cohort study of 672 girls with one prior cesarean part present process trial of labor. Yap retrospectively evaluated 38,027 deliveries occurring at a single tertiary care institution and found 21 circumstances of uterine rupture; 17 occurred after a historical past of a previous cesarean delivery (Herbst and K�ll�n, 2008). The two neonatal deaths that occurred had been a results of prematurity (23-week-old fetus) and a number of congenital anomalies; all live born infants had been discharged from the hospital without neurologic sequelae. However, all deliveries occurred in a tertiary care establishment with readily available obstetric anesthesiologists, neonatologists, and obstetricians. A third group of investigators retrospectively identified 99 circumstances of uterine rupture occurring over a period including 159,456 births (Hillier and Johanson, 1994). There were six neonatal deaths, however four of these occurred in women with uterine rupture at admission, and thus have been never given a trial of labor. Moreover, many of those women had an undocumented prior scar, which in some establishments would warrant an elective repeated cesarean section. The aforementioned current study evaluating 20,095 ladies with a previous cesarean delivery and their subsequent danger of rupture discovered a neonatal mortality of 5. However, as a outcome of this was a population based mostly examine, it was not specified whether or not these deliveries occurred in tertiary care establishments with the potential of performing emergent operative rescue procedures in the occasion of uterine rupture. Careful documentation of the knowledgeable consent and labor management should be accomplished. This heterogeneous term encompasses umbilical cord prolapse, by which the cord delivers via the cervix and compression by a fetal part ends in a considerably elevated danger of asphyxia; it additionally contains such entities as wire entanglements or "true knots," which may result in fetal compromise. One giant population-based examine compared 709 cases of cord prolapse occurring amongst 313,000 deliveries to matched controls and found that low birthweight, male sex, a number of gestations, breech presentation, and congenital anomalies all increased the risk of umbilical wire prolapse (Ali and Norwitz, 2009). Not surprisingly, twine prolapse was related to a high mortality rate (10%) that was reduced if cesarean somewhat than vaginal supply was carried out. The standard of care in cases of cord prolapse is to proceed instantly with cesarean section as quickly as possible while an assistant elevates the presenting fetal half with a vaginal hand to prevent compression of the umbilical cord. It can additionally be of paramount significance to have applicable pediatric help obtainable on the time of supply, as a result of the newborn is likely to be depressed and require resuscitation. Cord accident, or in utero compromise, secondary to entanglement of the umbilical cord as a scientific entity is tough to perceive. It is tempting to attribute the demise to an occasion that compromises umbilical blood circulate to the growing pregnancy. Hershkovitz et al (2001) recognized 841 circumstances of true knots from a inhabitants of 69,139 deliveries (for a prevalence of 1. Examination of the fetus exhibits the wire wrapped tightly across the torso, leg, and ankle, suggesting cord accident as a reason for demise. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: Vaginal delivery after cesarean part. Prapas N, Kalogiannidis I, Masoura S, et al: Operative vaginal supply in singleton term pregnancies: short-term maternal and neonatal outcomes, Hippokratia 13:41-45, 2009. Thorngren-Jerneck K, Herbst A: Low 5-minute Apgar rating: a population-based register research of 1 million time period births, Obstet Gynecol 98:65-70, 2001. Rosen this chapter introduces some of the scientific background and medical techniques used in providing obstetric analgesia and anesthesia. These practices provide substantial profit to the patient in labor and are essential for operative supply. These fibers pass by way of the paracervical tissue and course with the hypogastric nerves and the sympathetic chain to enter the spinal twine at T10 to L1. During the primary stage of labor (cervical dilation), the majority of painful stimuli are the end result of afferent nerve impulses from the decrease uterine segment and cervix, in addition to contributions from the uterine body causing visceral ache (poorly localized, diffuse, and normally described as "a uninteresting but intense aching"). These nerve cell bodies are situated within the dorsal root ganglia of ranges T10 to L1. During the second stage of labor (pushing and expulsion), afferents innervating the vagina and perineum trigger somatic ache (well localized and described as "sharp"). Pain during this stage is brought on by distention and tissue ischemia of the vagina, perineum, and pelvic flooring muscle tissue, associated with descent of the fetus into the pelvis and supply. Pain stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, elevates plasma catecholamine levels, creates reflex maternal tachycardia and hypertension, and reduces uterine blood circulate. In addition, modifications in uterine exercise can occur with the speedy lower in plasma epinephrine concentrations associated with onset of neuraxial analgesia. Oscillations in epinephrine may find yourself in a range of uterine results from a transient interval of uterine hyperstimulation (Clarke et al, 1994) to a transient period of uterine quiescence, or conversion of dysfunctional uterine activity patterns associated with poorly progressive cervical dilation to extra regular patterns associated with normal cervical dilation (Leighton et al, 1999). Fanny Longfellow, spouse of Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, was the first American to obtain anesthesia for childbirth, publicly proclaiming in 1847, "This is definitely the greatest blessing of this age" (Longfellow and Wagenknecht, 1956). The nice debate was largely settled four years later when Victoria delivered her ninth and last child, and the utilization of a royal anesthetic was acknowledged. Although many physicians had remained opposed, public opinion had modified and ladies have been requesting labor analgesia from their doctors. During the second half of the 20th century, anesthesiologists made important advances in techniques and improved safety for delivering labor analgesia. Hingson and Edwards (1943) developed the continual caudal catheter that preceded development of the epidural catheter. Apgar (1953) initially proposed a easy neonatal scoring system as a guide for evaluating the effects of obstetric anesthesia and later as a information for neonatal resuscitation. Other early pioneers within the rising specialty of obstetric anesthesia had been Gertie Marx (Marx and Orkin, 1958), John Bonica (1967), and Sol Shnider et al (1963).
Purchase pyridostigmine overnightIn a review of 26 cases reported between 1952 and 1980, 12 (46%) patients died, 9 of whom had been untreated but with a analysis made at post-mortem. Boyer K: Diagnostic testing for congenital toxoplasmosis, Pediatr Infect Dis J 20:59-60, 2001. McLeod R, Kieffer F, Sautter M, et al: Why stop, diagnose and treat congenital toxoplasmosis Rabilloud M, Wallon M, Peyron F: In utero and at delivery analysis of congenital toxoplasmosis: use of chance ratios for scientific administration, Pediatr Infect Dis J 29:421-425, 2010. World Health Organization Department of Reproductive Health and Research: the global elimination of congenital syphilis: rationale and technique for action: 2007. Menendez C, Mayor A: Congenital malaria: the least known consequence of malaria in being pregnant, Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 12:207-213, 2007. Hageman J, Shulman S, Schreiber M, et al: Congenital tuberculosis: crucial reappraisal of clinical findings and diagnostic procedures, Pediatrics 66:980-984, 1980. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines, 2010. It is thought that some subclinical infections of the fetus, amniotic fluid, membranes, or placenta may contribute to the onset of preterm labor and the delivery of preterm infants. There are a number of mechanisms by which bacteria can reach the fetus or newborn and initiate infection. Maternal blood stream infections, caused by micro organism similar to Listeria monocytogenes and Mycobacterium tuberculosis, can reach the fetus and cause an infection. Early-onset bacterial sepsis remains a major reason for neonatal morbidity and mortality, though the sepsisassociated dying charges per one hundred,000 reside births have declined considerably from 2001-2011. Much of this decline in mortality is because of the introduction of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis in pregnant women during labor and supply (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2007, 2009; Schrag et al, 2002; Schrag and Stoll, 2006). Mortality charges in infected untimely infants and really immature infants are significantly larger than in term infants. Major improvements in neonatal intensive care and early identification and recognition of infected infants have all contributed to lowered mortality charges within the newborn interval. The major portals of entry seem to be the respiratory tract, as suggested by the excessive frequency of acute respiratory misery and pneumonia, which occurs in infants with early-onset disease. Acquisition by way of the placenta is usually recommended in some instances by the presentation of high-grade bacteremia and severe sepsis clinically obvious on the time of start within the presence of intact membranes in infants born via cesarean part. Bacteria can initially spread into the choriodecidual house and may sometimes cross intact chorioamniotic membranes. Although many microorganisms recovered from the amniotic cavity are thought to induce spontaneous preterm labor, and presumably untimely rupture of membranes, the precise mechanisms by which this will likely occur are debatable. Clinical or subclinical chorioamnionitis can incite a marked inflammatory response with the release of cytokines that can contribute to the onset of preterm labor and untimely rupture of membranes. Other threat components for clinical intraamniotic infection include young maternal age, extended labor, prolonged rupture of membranes (18 hours), inner scalp fetal monitoring, the presence of urinary tract infections, and a history of bacterial vaginosis (Newton et al, 1989; Soper et al, 1989). Despite inherent antibacterial properties in amniotic fluid, these may not be sufficient to overcome a big bacterial inoculum, because of rapid multiplication of micro organism throughout a protracted labor or the absence of type-specific maternal antibodies for varied pathogens (Ferrieri, 1990). Infants who immediately display indicators of respiratory distress and after start undoubtedly have onset of an infection earlier than or throughout labor and supply. Particularly with hypoxia in utero, the toddler may gasp and inhale contaminated amniotic fluid, resulting in pneumonia, blood stream an infection, sepsis, and a severe systemic response syndrome. Infants who show such signs at start or inside a brief time after birth have the highest mortality charges. An overarching mechanism for continued bacteremia is the absence of enough native and systemic host defenses, such as enough complement ranges or type-specific immunity towards the invading microorganism (Ferrieri, 1990). Ideally, proinflammatory and antiinflammatory cytokines can be balanced; nevertheless, that is normally not the case and the micro organism stick with subsequent consequences. It is frequent in new child infants and, notably in preterm infants, to have dissemination of micro organism to other organs such because the meninges, kidneys, and bone. There have been modifications in the kinds of bacteria answerable for neonatal an infection through the years. In the Thirties and Nineteen Forties, the group A streptococcus was a prominent explanation for neonatal sepsis; this organism is now rather uncommon (Bizzarro et al, 2005). In the Fifties, nursery outbreaks of Staphylococcus aureus infections appeared across North America and Europe, prompting changes in techniques of hygiene and encouraging the development and use of penicillinase-resistant antibiotics (Bizzarro et al, 2005). Regional variations exist, nonetheless, and must be thought-about earlier than attempting to apply epidemiologic information to particular person perinatal items. For instance, Listeria monocytogenes is a frequent isolate in some western European international locations, and S. Stratified by race, the incidence elevated significantly among black infants from 2003 to 2006 (from zero. Early-onset illness amongst full-term white infants was secure during 2003 to 2006, whereas time period black infants had a major increase of the incidence throughout this era, from 0. When stratified by race, late-onset illness incidence among black infants decreased considerably by 42% from 2005 to 2006 (0. Between 2003 and 2006 there were no important developments amongst black or white infants. Infants described with early-onset sepsis frequently have a number of identifiable risk factors (Dutta et al, 2010). Prematurity is taken into account the one greatest risk issue for early-onset bacterial infections. Other threat elements for early-onset sepsis are maternal age, health and vitamin, colonization with well-known pathogens. In these situations, the mom generally displays signs and signs of chorioamnionitis, although it could happen within the absence of maternal signs (Baker and Edwards, 1995). The most widely used selective medium is Todd-Hewitt broth with either gentamicin or colistin and nalidixic acid. Although dearer than traditional culture-based detection assays, the outcomes are available 1 to 2 days sooner. However, girls with heavy (3+ to 4+) colonization, determined by semiquantitative assessment of vaginal or rectal cultures, usually have a tendency to pass the microorganism to their infants (Ancona et al, 1980). If a mother is allergic to penicillin however not at excessive danger for anaphylaxis, the use of cefazolin has been proposed (Schrag et al, 2002). It is therefore essential to have antibiotic testing done on the group B streptococcal isolates from pregnant women. Group B Streptococcal Sepsis in Neonates the vast majority of infections in newborn infants occur inside the first week of life and are designated as early-onset disease (Table 39-1). Late-onset infections occur in infants 7 days or older, with the majority of these infections appearing within the first three months of life. The frequency of meningitis, osteomyelitis, or septic arthritis is greater among infants with late-onset disease.

Buy pyridostigmine 60mg without a prescriptionBabies are warmed uniformly, regardless of their place on the bed platform surface, which may be rotated 360 degrees, accommodating intravenous and ventilator tubing and hooked up wire leads. The same platform tilts up to 12 levels in Trendelenburg or reverse Trendelenburg positions. Three-sided entry from drop-down walls within the radiant warmer mode facilitates procedures similar to diaper and bedding changes, blood sampling, starting intravenous lines, performing tracheal intubation, administering drugs, creating radiographs, and conducting ultrasound examinations with out interrupting warming. In considered one of a number of industry sponsored research, Leef et al (2001) reported that infants were dealt with considerably less with the Giraffe OmniBed, especially when converted to incubator mode (from 6. Consequences of such stimulation are unknown, though it appears reasonable to avoid extreme dealing with and inappropriate touches due to documented physiologic effects of procedural dealing with (Gressens et al, 2002). In a second industry-sponsored study (Gaylord et al, 2001), there were no differences found in mean skin temperature among the many 4 examined situations in premature neonates (R = radiant warmer configuration of OmniBed; transition R to C = convection-warmed closed OmniBed and transition C to R). These authors conclude that the Giraffe OmniBed supplied thermal and physiologic stability throughout bed states, eliminating the chance of toddler mishap because of bed switch. When transforming the Giraffe OmniBed from incubator to hotter bed and back, the closed-convection heat partition adapts to type a uniform open-radiant heating configuration with sequential alterations of air warming temperature, fan power, and radiant heat delivered whereas displaying all tools and child parameters in one management panel. For instance, when returning to the closedconvection mode, the retracting radiant hotter pylon instantly disconnects electrical power to the warming factor and opens a mechanical air vent to cool the reflector hood, avoiding overheating the infant upon descent. In closed-convection configuration, bidirectional airflow through a double wall development supplies a stably enclosed thermal environment. Light and sound levels are carefully controlled inside the OmniBed to promote toddler health and growth (Lynam, 2003). The WhisperQuiet mode limits sound to create probably the most quiet and soothing surroundings possible. In addition, servo-regulated humidification is equipped within the closed-incubator situation and could be set to a determined relative humidity between 70% and 80%, which is perfect to keep away from excessive insensible water loss and electrolyte disturbances often experienced by premature neonates with extremely low birthweight within the first week of life when incubated dry. One latest non�industry-sponsored report of a clinical sequence compared the usage of preliminary stabilization of babies with extremely low birthweight (<1000 g) beneath a radiant warmer followed by conventional incubation-dry versus use of humidity management in OmniBeds. The Giraffe Humidifier immerses a heating component in a reservoir of sterile, distilled water. Water temperature at equilibrium ranges 52� to 58� C, which is bactericidal to most organisms thriving at temperatures of 20 to 45� C (most human pathogens). In a third industrysponsored study by Lynam and Biagotti (2002), humidified OmniBeds (in vitro, air management mode at 35� C, and humidified to 65% relative humidity) have been cultured after investigator inoculation with reservoir contamination with four waterborne pathogens over a 4-week incubating period. In rare instances, partial detachment of the pores and skin thermistor probe can lead to life-threatening hyperthermia. A bigger, randomized trial of this system was carried out, confirming the prevention of heat loss with a polyethylene bag however not the advance in mortality (Vohra et al, 2004). Porat and Brodsky (1993) and Bhandari et al (2005) demonstrated that an adherent polyurethane layer over the torso and extremities of infants with very low birthweight improved fluid and electrolyte balance, decreased the occurrences of patent ductus arteriosus and intraventricular hemorrhage, and improved survival. Use with humidity-a approach typically referred to as swamping, which has never been validated-encourages bacterial colonization with water born pathogens. The blanket prevents convective heat loss and is thin sufficient to transmit almost fully radiant heat from the hotter. The plastic acts as a mechanical barrier to forestall convective turbulence from disrupting this microenvironment. A two-thirds discount in insensible water (and evaporative heat) loss underneath radiant warmers is prevented, resulting in less servo-controlled radiant heat supply required to maintain physique temperature in even the smallest infants. This discount exactly matches the oxygen consumption cost of utilizing radiant heaters reported by LeBlanc (1982). Anecdotal stories recommend that bacterial infections may very well be extra common with use of this method. Early studies instructed a major reduction in early mortality and morbidity in untimely infants weighing lower than 1. Behavioral research demonstrated more stable sleep patterns, less irritability at 6 months of age, and more eye contact with caregivers in infants nursed with kangaroo care. Kangaroo care has been proven to promote a thermal-neutral metabolic response and temperature stability in stably growing untimely babies. Moreover during kangaroo care, infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia have better oxygenation, and different infants show much less periodic respiratory and lowered apnea. In the fashionable nursery, kangaroo care be initiated throughout mechanical ventilation in uncomplicated sufferers. The toddler must be placed between breasts with most skin contact and ought to be coated with a blanket to avoid outward convective and evaporative heat losses. After initial sessions of 30 minutes to 1 hour with cautious intermittent temperature monitoring, intervals as much as 4 hours could also be achieved successively. Discussion Temperature maintenance of an especially untimely infant must be part of resuscitation from the time of delivery. Low admission temperature correlates with increased mortality charges in these infants. They are born wet and prone to extreme transepidermal evaporative and convective heat losses. In addition, heat loss may be exacerbated by suboptimal radiant heating; blowing noncontrolled heat, humidified air under plastic blankets, which is probably not as effective as the nonetheless air envelope conserved by the blanket; and the pressure for performing procedures with surgical drapes that block radiant heat supply. Quick drying, correct placement directly beneath the radiant heater at birth, and masking the pinnacle are small but necessary steps of temperature resuscitation. Other strategies could be considered from delivery, such a use of a plastic bag described by Vohra et al (1999) or a plastic blanket or polyurethane drape throughout umbilical catheterization. Cold-stressed infants ought to most likely be nursed underneath a servo-controlled radiant heat source, and heat loss must be minimized. During rewarming the infants should be carefully monitored, and warmth supply ought to be servo controlled. Alternatively, a preheated and humidified incubator can be used to rewarm infants, although the rate may be slower. Hybrid incubators that can also be used as radiant warmer beds are available and are helpful in rewarming eventualities. The child was resuscitated under a radiant hotter and dried, and a stocking cap was placed over the top. On arrival, the baby was weighed rapidly and positioned onto a preheated radiant hotter bed. Skin probe (servo control) temperature registered 33� C, with a rectal temperature of 35� C and axillary temperature of 34� C. The radiant hotter set point was targeted at 37� C, and temperatures have been monitored each quarter-hour. Heated and 100% humidified air from a respiratory pack was run underneath the blanket. The baby was transferred into a preheated and humidified incubator regulated by a skin probe set at 37� C. Two gentle bulbs (250 W) were positioned over the incubator hood for supplemental warmth and for warming throughout any process requiring opening the incubator. Over the next 12 hours the child had difficulty maintaining temperature regardless of incubator air temperature operating close to a set temperature of 37� C, and generally larger than 38. Craig (1963) outlined neonatal pyrexia as a rectal (core body) temperature higher than 37.
Buy discount pyridostigmine on-lineIn the classic evaluation of 49 infants with congenital malaria reported within the United States between 1950 and1992, the mean age at onset of symptoms was 5. Alternatively, the delay could also be attributed to the presence of transplacentally acquired maternal antimalarial antibodies. When such antibodies are current in enough concentrations, as in infants born to immune moms, parasitic replication can be prevented or attenuated, and clinical signs can be delicate, delayed, and even absent. The presence of a excessive focus of fetal hemoglobin in newborns may also promote resistance to multiplication of parasites. Among infants born to moms with low or nonexistent immunity, parasitic replication is more likely uninhibited, and medical signs of malaria might supervene. In a review of premature neonates with congenital malaria, four of 5 infants received a diagnosis within the 1st week of life (Ahmed et al, 1998), though the immediate medical analysis afforded these infants may have facilitated earlier detection. The clinical features of congenital malaria are nonspecific and often resemble these of bacterial or viral sepsis and other congenital infections. Fever is almost uniformly current, although without the classic paroxysmal sample described for malaria beyond the neonatal period. Hulbert (1992) noted fever in all forty four infants for whom clinical info was out there. In the instances reported from 1966 to 2005, fever was reported in 70 of 81 cases (86%) (Lesko et al, 2007). Hepatomegaly and splenomegaly suggestive of a transplacentally acquired an infection are present in a substantial portion of infants (Table 38-7). Anemia (often hemolytic), thrombocytopenia, and hyperbilirubinemia are essentially the most commonly reported laboratory findings. In endemic areas, the normal belief has been that congenital malaria is uncommon and that when it occurs the toddler is typically asymptomatic and develops no medical features. Depending on the region, spontaneous clearance of peripheral parasitemia has been documented in 87% to one hundred pc of neonates (Lesko et al, 2007; Mukhtar et al, 2006). Larkin and Thuma (1991) discovered peripheral parasitemia inside 24 hours of age in 19 of fifty one newborns (65%), but only 7 had scientific signs of illness. More lately, Falade et al (2007) famous spontaneous clearance of parasitemia in 62% of 95 neonates before day 2 of life. Of the remaining infants, 34% had been symptomatic within 3 days of birth, with fever and refusal to eat being the most typical signs of disease. When lively surveillance for malaria was conducted in newborns being evaluated for possible bacterial sepsis in Nigeria, 16 of 203 (8%) neonates had parasitemia, and 10 (5%) met the definition of congenital malaria (Ibhanesebhor, 1995). Predominant options of disease included fever, respiratory misery, anemia, and hepatomegaly. In one other area in Nigeria, of 202 neonates much less youthful than 1 week who had been admitted for evaluation of sepsis, 71 (35%) had been recognized with congenital malaria (Ekanem et al, 2008). Definitive diagnosis of congenital malaria is based on the microscopic demonstration of parasites on stained thick and skinny blood movies. Thick blood smears take a look at for the presence of parasites by concentration of red blood cells, whereas skinny blood smears permit species identification and quantification of parasitemia. In instances of suggested congenital malaria, specimens for smears must be obtained from both the toddler and the mother. If test results from the initial set of smears are unfavorable, extra units ought to be obtained every 12 to 24 hours; three sets are typically considered sufficient for diagnostic analysis. Response to therapy may also be measured by clearance of parasitemia on blood movies. However, the tests have demonstrated blended results in a quantity of trials, and sensitivity stays an issue, particularly at low parasite densities. Information regarding the sensitivity of those exams is restricted for neonatal or congenital malaria. As with malaria normally, the prognosis of congenital malaria outdoors of endemic areas is commonly delayed because of nonspecific options and lack of scientific suspicion. In all four cases of congenital malaria reported by Quinn et al (1982), Plasmodium spp. Maternal history of current travel to or emigration from an endemic area might counsel the analysis, but is commonly obscured by the shortage of clinical or laboratory findings in the mom. Lesko et al (2007) found that, of the moms for whom a history was obtainable, 67% reported having fever during being pregnant, and 26% reported a diagnosis of malaria throughout pregnancy. Maternal blood films have been performed after both symptomatic sickness or malaria prognosis in the toddler. Further confounding the early recognition of disease in the toddler is the possibly prolonged lapse between malaria publicity in the mom and transmission of infection to the toddler. Of 11 infants with congenital malaria within the United States born to ladies known to have parasitemia at or shortly after delivery, solely 5 underwent testing by blood smears, and all 5 had adverse test outcomes at the time of supply (Lesko et al, 2007). Data are inadequate to decide the overall threat of an toddler developing congenital malaria when born to a girl in danger for parasitemia or recognized with parasitemia at delivery. Consequently, the analysis of infants born outside endemic areas to girls with epidemiologic risk components for parasitemia should be individualized. Information regarding treatment of congenital malaria is restricted, and really helpful chemotherapy is much like that of noncongenital infections. The therapy routine is predicated on the infecting species, the potential for drug resistance, and the severity of illness. In older youngsters, three treatment choices currently really helpful are: (1) oral quinine plus either tetracycline, doxycycline, or clindamycin; (2) atovaquone-proguanil; or (3) mefloquine. For the therapy of congenital malaria, oral quinine sulfate and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for five days was really helpful by Quinn et al (1982), who used the regimen to treat a 1-month-old toddler. Other regimens used successfully in neonates embrace oral quinine sulfate and pyrimethamine-sulfadoxine (Gereige and Cimino, 1995) and intravenous quinine hydrochloride adopted by oral quinine (Airede, 1991). Management of severe malaria includes parenteral treatment in an intensive care setting. Until just lately, the only parenteral therapy obtainable in the United States was quinidine gluconate. Quinidine is more cardiotoxic than quinine and should be administered with steady cardiac monitoring. Exchange transfusion could also be warranted when parasitemia exceeds 10% or if there are issues at decrease parasite densities. It has been instructed that infants born to mothers with parasitemia at supply ought to be treated presumptively for congenital malaria (Lesko et al, 2007). Data are insufficient to decide the danger of an infant creating congenital malaria when born to a mother with parasitemia. It is really helpful that physicians choose every case individually, contemplating elements such as entry to medical care and reliability of follow up in deciding whether to deal with infants presumptively. In a review of studies printed between 1985 and 2000, Steketee et al (2001) decided population-attributable risks for maternal malaria of 3% to 8% for toddler mortality. It was estimated that seventy five,000 to 200,000 toddler deaths annually are related to malaria during pregnancy, although what quantity of these are related to congenital malaria is unknown.
Buy pyridostigmine 60mg low priceDrug concentrations measured serially are graphed on semilogarithmic axes, and the best-fit line is decided both visually or by linear regression evaluation. In this illustration of first-order kinetics, the concentration decreases 50% (from 800 to 400) through the first hour and decreases one other 50% (from 400 to 200) through the second hour. More drug is eliminated during one half-life at greater concentrations, although the proportion removed stays constant. Two exponential terms are wanted to describe the change in concentration over time, as: C = Ae - t + Be - t the place k = zero. An initial speedy decrease in concentration is the distribution () phase, typically lasting 15 to forty five minutes, which is adopted by a sustained slower fee of elimination, the elimination () part. Such biphasic processes are greatest visualized from semilogarithmic graphs of focus versus time. When such semilogarithmic graphs present In this equation, the rate fixed for distribution is designated to discriminate it from the speed fixed for terminal elimination (), where A and B are the time = 0 intercepts for the strains describing distribution and elimination, respectively. The fee fixed of distribution () can be determined by plotting the distinction between the whole amount of drug misplaced initially and the quantity of drug misplaced by way of elimination (Greenblatt and Koch-Weser, 1975). The noticed rates often symbolize the summation of several simultaneous processes, each with differing charges, occurring in varied tissues. When the time course of drug elimination is observed for prolonged periods, a 3rd rate of elimination, or section, may be noticed and is often attributed to elimination of drug that has reequilibrated from deep tissue compartments back into the plasma. The kinetics of a drug are expressed with the smallest variety of compartments that precisely describe its concentration adjustments over time. The adjective obvious is used as a result of cautious research often shows that distribution occurs although the kinetic curve has only a single slope. Single-compartment kinetics implies that the drug quickly and fully distributes homogeneously all through the physique, which not often happens clinically. If sampling begins after the distribution part, the concentration time factors might fit a single-compartment, first-order model, which determines the elimination rate constant (). The extra clinically limited but correct approach to kinetic analysis, noncompartmental analysis, makes no assumptions about the variety of compartments (Rowland and Tozer, 2010). For medicine exhibiting zero-order kinetics, small increments in dose may cause disproportionately giant increments in serum concentration. Certain drugs administered to newborns exhibit zero-order kinetics at therapeutic doses, and concentrations and have to be recognized for his or her potential accumulation (Box 34-2). Estimation of the elimination half-life is usually accomplished using the slope of the log transformed focus measurements made during the end of a pharmacokinetic study. This relationship may be expressed as: dC dt It is necessary to understand when zero-order kinetics occurs, the way to acknowledge it, and the way it affects drug concentrations. Zero-order kinetics is usually referred to as saturation kinetics, as a outcome of it may possibly occur when excess amounts of drug utterly saturate enzymes or transport techniques in order that they metabolize or transport solely a continuing amount of drug over time. The population method describes the concentration-versus-time profile for all of the patients enrolled in a given study simultaneously, estimating inhabitants parameters that describe the overall pharmacokinetic profile of the entire study group and affected person particular parameters that outline the individual patients in the examine. For instance, one group of 28- to 32-week premature infants might have samples drawn at 1, 4, and 12 hours, whereas one other group of 28to 32-week premature infants might be sampled at 0. The concentrations from these two teams of comparable sufferers are then analyzed in mixture to present data during both distribution and elimination phases, thus describing the kinetics with a restricted quantity of blood sampled from each affected person. Furthermore, the inhabitants strategy allows for the investigation of patient covariates of interest which may clarify differences seen inside the population of sufferers enrolled in the trial. Typical covariates corresponding to gestational age, gender, and disease circumstances may also be assessed for their contribution to differences seen between topics in a clinical research. These covariates can be helpful for gaining a better understanding of factors which will alter the pharmacokinetics of infants which may otherwise be thought-about comparable. The target website of drug action is normally inaccessible for monitoring concentrations. A specific concentration or range of circulating concentrations is correlated with the effective concentration at the website of action, which provides a "therapeutic" concentration range. The necessities for efficient and correct application of the target drug concentration remedy strategy in adults have been discussed by Spector et al (1988). When applied to newborns, these requirements spotlight the special issues of drug therapy in these patients and the special circumstances by which clinical drug concentration monitoring is appropriate. Patient response, not a specific drug concentration range, is the endpoint of remedy. Although concentrations of aminoglycoside antibiotics, corresponding to gentamicin, are monitored incessantly in newborns, toxicity is rare (McCracken, 1986). In newborns with critical therapeutic problems, measurement of serum drug concentrations must be used to achieve effective concentrations and to avoid toxicity. When the desired concentration range and kinetic parameters are known, doses may be estimated to attain that concentration with single bolus doses or bolus doses adopted by steady infusions. This equation could additionally be used to estimate dosage changes needed to increase or decrease focus. For the first dose, the beginning focus is zero; afterward, the calculation of distribution quantity ought to use the change () in focus from the previous trough to the height related to that dose. To reach a desired focus quickly, a loading dose can be administered adopted by a sustaining infusion. The two broad indications for monitoring drug where C = focus, Vd = quantity of distribution, and k = rate fixed of elimination. Steady state is reached when tissue concentrations are in equilibrium and the amount of drug eliminated equals the amount of drug infused. As famous during infusions, the size of time required to attain steady-state concentrations depends totally on the elimination half-life, not the dosing interval. Clearance is proportional to organ blood move and the intrinsic capacity of organs to metabolize or remove drug from the circulation. Clearance can be measured by the speed of appearance of drug outside the physique (similar to urinary creatinine clearance) or by the speed of disappearance of drug from the circulation in contrast with the circulating focus. Values for clearance and volume of distribution at different phases of preterm development can be found for a number of medicine and can be utilized to estimate the doses needed to achieve and preserve therapeutic concentrations related to desired clinical responses. Studies of the analgesic fentanyl illustrate the developmental changes in its kinetics and how they can be utilized to calculate dosages to reach and maintain concentrations associated with efficient analgesia. Analgesia has been related to a serum fentanyl focus of 1 to 2 ng/mL (Santeiro et al, 1997). If analgesic remedy is initiated with a steady infusion of fentanyl, five half-lives are needed to reach a gentle state. It is necessary to think about that if drug clearance decreases, the regular state focus throughout an infusion will increase proportionally. During repeated administration, the peak and trough ranges after every dose improve for a time. Steady-state, or plateau, concentrations are reached when the quantity of drug eliminated equals the quantity of drug administered during every dosing interval. During repetitive dosing, the steady-state concentrations achieved are associated to the half-life, dose, and dosing interval relative to the half-life (Buxton, 2006; Rowland and Tozer, 2010). Several important ideas of pharmacokinetics are illustrated on this determine; the arithmetic are described intimately elsewhere (Buxton, 2006). Drug concentrations rise and fall with drug administration (absorption) and elimination.
References - Escudier B, Bellmunt J, Negrier S, et al: Phase III trial of bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (AVOREN): final analysis of overall survival, J Clin Oncol 28:2144n2150, 2010.
- McCabe, M. (1998). Patient Self-Determination Act: A Native American (Navajo) perspective. Cambridge Quarterly of Healthcare Ethics, 3, 419n421.
- Murthy P, Cohn JA, Selig RB, et al: Robot-assisted laparoscopic augmentation ileocystoplasty and Mitrofanoff appendicovesicostomy in children: updated interim results, Eur Urol 68(6):1069-1075, 2015.
- Carrasquillo, O., Orav, E. J., Brennan, T. A., & Burstin, H. R. (1999). Impact of language barriers on patient satisfaction in an emergency department. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 4, 82n87.
- Cameron AP, Suskind AM, Neer C, et al: Functional and anatomical differences between continent and incontinent men post radical prostatectomy on urodynamics and 3T MRI: a pilot study, Neurourol Urodyn 34(6):527n532, 2015.
|
|