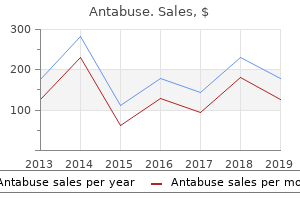
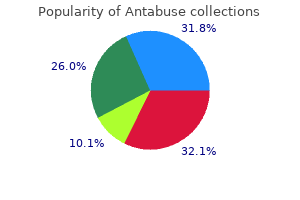
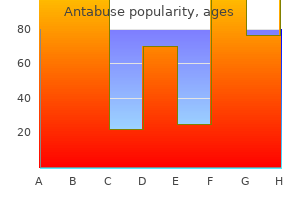
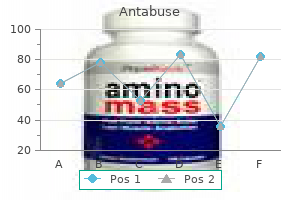
"Buy antabuse 250 mg overnight delivery, treatment 4 burns."By: Dawn Sowards Brezina, MD - Assistant Professor of Medicine
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/dawn-sowards-brezina-md
Generic 500mg antabuse with amexThis is followed by progressive somnolence related to seizures, extensor posturing, and disconjugate gaze. Some sufferers, particularly kids, have focal indicators related to cerebral infarcts or hemorrhage. Hypoglycemia, pulmonary edema, renal failure, bleeding diathesis, and hepatic dysfunction may complicate the course of the disease. ClinicalManifestations Neurological signs not often develop in immunocompetent hosts, though an acute encephalitis with headache, fever, irritability, seizures, and drowsiness progressing to coma happens in some circumstances. Immunocompromised hosts are also susceptible to an acute encephalitic syndrome or, extra regularly, a subacute disease characterised by focal indicators related to seizures and indicators of intracranial hypertension. Diagnosis In normal hosts, a fourfold rise in serum antibody titer is a sensitive indicator of acute infection. The sustained persistence of specific immunoglobulin M antibodies and high immunoglobulin G titers in a significant proportion of people within the general inhabitants complicates the serologic interpretation for discrimination between latent infection and energetic an infection, no matter their human immunodeficiency virus serologic standing. A brain biopsy must be performed if empirical therapy produces no clinical and neuroimaging improvement on repeated neuroimaging studies at 3 weeks. Neuroimaging findings are nonspecific and embody diffuse adjustments in white matter, hyperintensity in the basal ganglia, and ventricular enlargement. Perivascular demyelination of subcortical white matter and brain edema are seen is most instances. This arsenical drug produces a extreme reactive encephalopathy in about 10% of sufferers, half of whom die of it. The role of pretreatment with corticosteroids to forestall this reaction is unclear. Cerebral abscesses may happen and are most often located at the corticosubcortical junction, basal ganglia, and upper brainstem. Glial nodules composed of astrocytes and microglial cells are frequent within the surrounding mind tissue. American Trypanosomiasis Triatomine bugs ("kissing bugs"), discovered largely within the genus Triatoma, are the vector for Trypanosoma cruzi. These insects infect people by biting them to feed on their blood and defecating within the area. More hardly ever, an infection could be acquired through uncooked food contaminated with infected bug feces, from blood/organ donation, or congenitally from an infected mother. Clindamycin, clarithromycin, trimetrexate, piritrexim, and atovaquone are various medication in sufferers in whom skin reactions to sulfadiazine develop. In addition, immunocompromised sufferers can expertise reactivation of persistent infections, which ends up in a rapidly deadly meningoencephalitic syndrome similar to that noticed in acute infections. Invasion of arterial walls by trophozoites causes a necrotizing angiitis that will lead to cerebral infarcts. The earlier the therapy in the course of infection, the upper the chance of remedy. Amebic infections of the brain are highly deadly diseases with mortality exceeding 90%. After ingestion, the eggs mature into oncospheres, that are then carried into the tissues of the host, the place cysticerci develop. The most accepted regimens of cysticidal medicine are albendazole, 15 mg/kg per day for 1 week, and praziquantel, 50 mg/kg per day for two weeks. In one double-blind, placebocontrolled trial, albendazole was discovered to be secure and effective for the treatment of viable parenchymal mind cysticerci. In addition, the variety of cystic lesions that resolved was significantly higher in sufferers receiving albendazole. The elevated inflammation around degenerating cysts could exacerbate neurological symptoms. For this reason, corticosteroids ought to be routinely administered with cysticidal agents. In a latest research, albendazole combined with praziquantel significantly elevated cyst resolution in sufferers with multiple viable cysts,80 and one other research confirmed that resolution of all viable cysts is related to fewer partial seizures during an 18-month interval after remedy. These sufferers have to be managed with excessive doses of corticosteroids, osmotic diuretics, and decompressive craniotomy if essential. There are anecdotal reports of clinical enchancment with minimally invasive endoscopic resection of cisternal cysts with out problems regardless of intraoperative rupture of the cysts. The most common findings are cystic lesions displaying the scolex and parenchymal brain calcifications. Parenchymal brain cysts usually lodge in the cerebral cortex or the basal ganglia. Subarachnoid cysts are most commonly positioned within the sylvian fissure or within the cisterns on the base of the brain. Ventricular cysticerci could additionally be connected to the choroid plexus or could additionally be floating free in the ventricular cavities. Spinal cysticerci could also be found in both the twine parenchyma and the subarachnoid house. The inflammation round cysticerci induces modifications in cerebral tissues, including edema, gliosis, thickening of the leptomeninges, entrapment of the cranial nerves, angiitis, hydrocephalus, and ependymitis. Single big cyst arising from the sylvian fissure after parietal craniotomy with exposure of the sylvian fissure. Cyst was excised intact without proof of residual arachnoiditis or arteritis on surgical mattress. Because the affected person had no concomitant parenchymal or extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis, anthelmintic remedy was not required. On long-term follow-up, the affected person had not developed arteritis-associated stroke. Cysticerci arising from the fourth ventricle after a suboccipital craniectomy with publicity of the roof the ventricular cavity. Lesions often emerge intact after an induced Valsalva maneuver with the patient within the sitting position. The primary complication of a ventricular shunt is the excessive incidence of shunt dysfunction. The efficacy of this shunt was in contrast with that of a standard Pudenz-type shunt. After 1 yr of follow-up, withdrawal of the shunt was needed in 45% of patients with the Pudenz-type shunt but in solely 30% of those with the model new shunt. Hydrocephalus can also be managed with endoscopic foraminotomy and endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Ventricular cysts may be removed extra safely by surgical excision or endoscopic aspiration. The surgeon should think about the potential for cyst migration between the time of analysis and the surgical procedure, and such migration must be dominated out with a neuroimaging research before surgery to keep away from pointless craniotomies. Echinococcosis (Hydatid Disease) There are two major types of echinococcosis: cystic hydatid disease (caused by Echinococcus granulosus) and alveolar hydatid illness (caused by Echinococcus multilocularis). In the cycle of hydatid disease, a herbivore normally harbors the larvae, mostly in the viscera, and a carnivore turns into contaminated with the adult tapeworm by eating uncooked viscera.
Syndromes - Antacids
- Low blood pressure
- Nausea and vomiting
- Chromosomal studies for abnormalities in chromosome 11
- Excessive bleeding following circumcision
- Not feeling hungry and not eating
- Fever
- Disregard the feelings of others, and have little ability to feel empathy
- Chronic disease, such as congestive heart failure
- Vomiting
Buy antabuse nowFactors influencing wound therapeutic after surgery for metastatic illness of the backbone. Postoperative wound infection after instrumentation of thoracic and lumbar fractures. Spondylodiscitis after lumbar microdiscectomy: effectiveness of two protocols of intraoperative antibiotic prophylaxis in 1167 circumstances. Posterolateral endoscopic excision for lumbar disc herniation: surgical technique, outcome, and complications in 307 consecutive instances. Endoscopic transforaminal discectomy for recurrent lumbar disc herniation: a prospective, cohort evaluation of 262 consecutive instances. Suspended laminoplasty for wide posterior cervical decompression and intradural entry: outcomes, advantages, and issues. Prophylactic antibiotics and wound infections following laminectomy for lumber disc herniation. Complications, outcomes, and wish for fusion after minimally invasive posterior cervical foraminotomy and microdiscectomy. Management of deep wound infection after posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cages. Postoperative deep wound infection in adults after posterior lumbosacral backbone fusion with instrumentation: incidence and administration. The significance of positive cultures from orthopedic fixation units within the absence of clinical infection. Risk elements for the development of delayed infections following posterior spinal fusion and instrumentation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients. Delayed infections following posterior spinal instrumentation for the remedy of idiopathic scoliosis. Implant elimination for latedeveloping infection after instrumented posterior spinal fusion for scoliosis: reinstrumentation reduces lack of correction. Infection with spinal instrumentation: evaluate of pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention, and management. Late operative website pain with isola posterior instrumentation requiring implant removal: an infection or metallic reaction Complications in thoracoscopic spinal surgical procedure: a study of 90 consecutive sufferers. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with unilateral pedicle screw fixation. Prevention and administration of intrathecal drug supply and spinal twine stimulation system infections. Identification and administration of intrathecal baclofen pump problems: a comparability of pediatric and grownup sufferers. Perioperative issues of posterior lumbar decompression and arthrodesis in older adults. Perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis in the gastric bypass patient: will we achieve therapeutic levels Body mass index as a predictor of complications and mortality after lumbar spine surgical procedure. Nutritional deficiencies after staged anterior and posterior spinal reconstructive surgery. Surgical website infections following spinal surgical procedure at a tertiary care center in Lebanon: incidence, microbiology, and danger elements. Glucose effects on skin keratinocytes: implications for diabetes skin complications. Continuous intravenous insulin infusion reduces the incidence of deep sternal wound an infection in diabetic sufferers after cardiac surgical procedures. Continuous insulin infusion reduces infectious issues in diabetics following coronary surgery. Perioperative normothermia to cut back the incidence of surgical-wound an infection and shorten hos- seventy seven. The influence of smoking on problems after main amputations of the decrease extremity. Smoking as a risk issue for wound therapeutic and infection in breast cancer surgical procedure. Abstinence from smoking reduces incisional wound infection: a randomized controlled trial. Multivariate evaluation of determinants of postoperative wound an infection in orthopaedic patients. Microbiological contamination of intraoperatively collected erythrocyte concentrate in mechanical autotransfusion in tumor surgery. Effect of perioperative blood transfusion and cell saver on the incidence of postoperative infective problems in patients with an aneurysm of the stomach aorta. Operative remedy of spinal deformities in sufferers with cerebral palsy or mental retardation. Deep wound infections after neuromuscular scoliosis surgery: a multicenter examine of threat elements and therapy outcomes. Spinal radiation before surgical decompression adversely affects outcomes of surgery for symptomatic metastatic spinal wire compression. Epidural abscess and discitis complicating instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a case report. Epidural abscess as a delayed complication of spinal instrumentation in scoliosis surgical procedure: a case of progressive neurologic dysfunction with complete restoration. Spinal epidural abscess: up to date trends in etiology, analysis, and administration. Quantitation of C-reactive protein levels and erythrocyte sedimentation price after spinal surgical procedure. Diagnostic and therapeutic administration of lumbar and thoracic spondylodiscitis-an evaluation of 59 cases. Fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography findings in spondylodiscitis: preliminary outcomes. Surgical web site infections in spine surgical procedure: identification of microbiologic and surgical characteristics in 239 cases. Postoperative spondylodiskitis: etiology, medical findings, prognosis, and comparison with nonoperative pyogenic spondylodiskitis. General rules in the medical and surgical administration of spinal infections: a multidisciplinary strategy. Management of infection after instrumented posterior spine fusion in pediatric scoliosis. Instrumentation of the infected and unstable spine: a review of 17 cases from the thoracic and lumbar backbone with pyogenic infections.
Buy antabuse 250 mg overnight deliveryPharmacist participation on doctor rounds and opposed drug events in the intensive care unit. Pharmacists on rounding groups cut back preventable antagonistic drug occasions in hospital common medication items. Effects of a clinical pharmacist service on health-related high quality of life and prescribing of medicine: a randomised managed trial. Effect of an electronic medicine reconciliation application and process redesign on potential adverse drug occasions: a cluster-randomized trial. Medication reconciliation: barriers and facilitators from the perspectives of resident physicians and pharmacists. Effect of admission treatment reconciliation on opposed drug events from admission treatment adjustments. Effect of Bar-code Technology on the Incidence of Medication Dispensing Errors and Potential Adverse Drug Events in a Hospital Pharmacy. Medication allotting errors and potential adverse drug events before and after implementing bar code know-how within the pharmacy. Sustaining reductions in catheter related bloodstream infections in Michigan intensive care units: observational study. Daily interruption of sedative infusions in critically ill patients undergoing mechanical air flow. A systematic review of the effectiveness, compliance, and important elements for implementation of security checklists in surgical procedure. Prevention of retained surgical sponges: a decision-analytic mannequin predicting relative cost-effectiveness. Effect of a 19-item surgical safety guidelines during pressing operations in a global patient inhabitants. Frequency and predictors of complications in neurological surgery: national developments from 2006 to 2011. Assessing the surgical and obstetrics-gynecology workload of medical officers: findings from 10 district hospitals in Ghana. Success in preventing wrong-site procedures in Minnesota with the Minnesota Time Out. University of California, Los Angeles, surgical time-out course of: evolution, challenges, and future perspective. Systematic evaluation and metaanalysis of the impact of the World Health Organization surgical safety guidelines on postoperative complications. Intrawound vancomycin to forestall infections after backbone surgery: a systematic evaluation and metaanalysis. Effectiveness of local vancomycin powder to lower surgical site infections: a metaanalysis. Surgical web site an infection in spinal surgery: a comparative research between 2-octyl-cyanoacrylate and staples for wound closure. Negative strain wound therapy reduces incidence of postoperative wound infection and dehiscence after long-segment thoracolumbar spinal fusion: a single institutional expertise. Risk factors for surgical web site an infection following spine surgical procedure: efficacy of intraoperative saline irrigation. Prevention of post-operative infection in backbone surgery by wound irrigation with a solution of povidone-iodine and hydrogen peroxide. Transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary tumors in the United States, 1996-2000: mortality, morbidity, and the results of hospital and surgeon volume. Variability in consequence after elective cerebral aneurysm restore in high-volume academic medical facilities. Patient outcomes are better for unruptured cerebral aneurysms treated at facilities that preferentially deal with with endovascular coiling: a research of the national inpatient sample 2001-2007. Surgeon quantity as an indicator of outcomes after carotid endarterectomy: an impact unbiased of specialty apply and hospital volume. The impression of supplier volume on the outcomes after surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. Relationship between mortality charges and hospital patient quantity for Medicare sufferers present process major orthopaedic surgical procedure of the hip, knee, backbone, and femur. The vestibular schwannoma surgical procedure studying curve mapped by the cumulative summation test for studying curve. Learning curve and issues of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Lam the preanesthetic analysis may be performed well in advance of the deliberate surgical procedure for many elective procedures throughout a visit to the preanesthetic evaluation clinics. It may be carried out at the bedside in the hospital ward or intensive care unit the "evening before" for inpatients. For pressing and emergency procedures, a brief, focused preanesthetic evaluation is carried out just earlier than surgery. In short, the preanesthetic evaluation is crucial to ensure affected person security, good surgical outcomes, patient satisfaction, and reduction of well being care costs. It is essential, subsequently, that a timely preanesthetic analysis be planned for all neurosurgical patients. The preanesthetic evaluation is defined because the scientific evaluation that precedes the delivery of anesthesia take care of surgical and nonsurgical procedures. Other benefits are improved security of perioperative care, optimum useful resource utilization, and higher outcomes and affected person satisfaction. Establishment of rapport with the patient and quick family members/significant others in order to minimize their anxiety and to have a cooperative and relaxed patient. Provision of data to the affected person and household relating to anesthetic methods and procedures and the associated dangers and advantages, postoperative administration points together with pain management, and the attainable want for postoperative mechanical air flow in main procedure. Complete evaluate of medical, surgical, and anesthetic history and present medicines, thus establishing a baseline profile. General bodily examination, together with recording of important indicators and examination of particular person systems, significantly the nervous and cardiopulmonary methods. Interpretation of related laboratory data, arrangements for further investigations and consultations if deemed needed, and elimination of unnecessary preoperative standing "screening tests," to restrict investigations to only appropriate ones. Stratification of patient danger relating to morbidity and mortality primarily based on the previous considerations. Formulation of an anesthetic plan, group of sources for perioperative care, and postoperative restoration. Documentation of knowledgeable consent for the proposed anesthetic technique and procedures. The expected metrics include improved operational efficiencies, decreased useful resource utilization, a reduction in length of keep and readmission, and a decrease in issues and mortality-resulting in a better affected person experience of care. Examples embrace (but not limited to) ruptured abdominal/thoracic aneurysm, large trauma, intracranial bleed with mass effect, ischemic bowel within the face of great cardiac pathology or multiple organ/system dysfunction. A good starting point is the primary disease course of requiring surgical intervention, which can alert the anesthesiologist to potential issues, such as trauma and a full abdomen, head damage and the event of coagulopathy, and intracranial aneurysm and the need for blood stress management.
Buy 250 mg antabuse free shippingConservative flap size and avoidance of extension of the flap beyond midline in tissues with poor vasculature similar to irradiated tissue or in elderly sufferers are really helpful. Given enough blood provide, simplest scalp wounds ought to heal without complication. The defect dimension, neurovascular anatomy, and high quality of the encompassing tissue could restrict the options for reconstruction. Important considerations embrace the size of the defect, the particular tissues missing (bone, pericranium, galea, skin), the state of the surrounding tissue. The simplest technique of closing a wound is by secondary intention-allowing the defect to shut and contract by itself. The diameter of the defect that can shut this fashion is partly dependent on the laxity of the surrounding tissue, however within the scalp, closure of defects up to approximately 3 cm in diameter could be achieved with moist dressing change assist. This may be most well-liked over main closure in contaminated, traumatic wounds of the scalp, in these with a delayed presentation, or in high-risk medically advanced sufferers. Although these wounds can contract additional in the course of the healing course of, the timing could additionally be prolonged and the scars are affected by persistent alopecia, which can make the defects extra noticeable. Vacuum-assisted closure can also be used in wounds healing by secondary intention and has been proven to decrease wound bacterial load. Monofilament suture is a single-strand suture with confirmed resistance to ingress of micro organism as in contrast with multifilament braided suture, which might, in theory, allow bacteria to harbor in its interstices. Braided, multifilament suture, on the opposite hand, has the benefit of increased tensile strength and often flexibility. Absorbable suture offers temporary wound help, which is gradually damaged down by way of enzymatic or hydrolytic degradation. For floor closure, everlasting suture can provide added strength over the first few days or perhaps weeks postoperatively. The best suture diameter is the smallest suture capable of reaching a tension-free closure to reduce foreign body influence, which can potentiate infection. The thick skin of the scalp is significantly much less cellular than in different parts of the physique. Less tensile stretch can result in improved wound healing with much less wound breakdown (necrosis and dehiscence) and a thinner, extra cosmetic scar. The deeper galeal tissue bears nearly all of the stress and requires a suture materials with applicable tensile energy and low reactivity. Absorbable suture with a moderate half-life (at least 6 to eight weeks) is good for buried galeal closure. An inverted, interrupted sew is the popular closure method as a end result of it avoids compromising the vessels throughout the galea that supply the overlying scalp. Vertical mattress, continuous, and locking sutures are normally discouraged within the galea as a result of they might impair the blood supply to the flap and the incision margin. As the hair grows back and the scar remodels, this will become even less noticeable. The overlying skin is finest closed with steady, running nonabsorbable monofilament suture to present wound help with minimal tissue response. With all suturing, the needle must be inserted perpendicular to the goal gentle tissue or skin edge, with an equal depth and distance taken on each side of the wound. In the skin, too, malalignment of incision edges can end result in an inverted scar that casts a shadow and draws extra visible attention to the scarred space as quickly as healed. They rely upon nutrients diffusing from viable, underlying tissue through the preliminary part of healing, a course of known as imbibition. Therefore a healthy layer of pericranium should remain intact for a skin graft to survive. Some have had success with burring down the outer desk of the calvaria to bleeding bone, restoring granulation tissue with a interval of vacuum-assisted closure or continuous moist dressings, after which inserting a pores and skin graft on this granulation tissue. However, in patients with significant medical comorbidities, this might be the appropriate treatment option. Initially, split-thickness pores and skin grafts had been used in reconstruction of scalp lesions. These have the benefit that large grafts can be harvested, with donor websites that can reepithelialize and heal on their very own. There is also less primary contracture in these grafts owing to fewer elastin fibers within the graft. However, splitthickness grafts have extra secondary contracture throughout therapeutic than full-thickness grafts and heal with a much less esthetically pleasing scar. The grafts, as quickly as healed, typically have a colour mismatch with the encompassing skin and, due to their decreased mobility, form a dense adherence to underlying tissue. C, Reconstruction with a split-thickness skin graft, used because of the large amount of pores and skin essential. However, the thick, inflexible nature of the scalp requires some superior planning. Broader-based, larger flaps are sometimes simpler to maneuver within the scalp than smaller flaps. Whenever flaps are deliberate based on the subdermal plexus in contrast to named perforator vessels, a more conservative flap design must be applied. Therefore, as a guideline, an approximate length-width ratio of 2: 1 permits an sufficient vascular inflow whereas supporting mobility of an area flap design. Local flap design on the scalp is restricted by the underlying vascularity and mobility of the tissues however has numerous variations revealed within the literature. Advancement flaps are designed to advance tissue mobilized on three sides into an adjacent defect by way of direct translation. Transposition flaps are much like rotational flaps, but a donor web site rotates over intact skin versus encompassing the complete area throughout the flap itself. Over the years, plastic surgeons have identified sure predictable transposition flaps, such because the rhomboid flap, utilizing a defined geometric basis. In the scalp, the thick nature of the tissue limits the usefulness of those smaller flaps. It is incessantly a better choice to excise these later, once the flap has proven its vascularity and healed in, versus threatening the viability of the entire flap for a small gain in contour. Local flaps based on named perforating vessels, such as the temporoparietal, occipital, and supraorbital arteries, present increased dependable size and adaptability in overlaying bigger defects. Tissue enlargement is a powerful device to enhance the quantity of hair-bearing scalp available for either primary closure or native flaps. It entails inserting a Silastic, expandable prosthesis beneath the adjacent galea and steadily filling the expander in a medical setting over the following weeks. A important melanoma resection (A) requiring a triple rhomboid flap combining a number of flaps to close this huge defect. Photos of outcomes are from the time of surgical procedure (B) and three weeks postoperatively (C). A mixture of a big galeal flap with a full-thickness pores and skin graft to reconstruct the donor site (A and B) yielding an acceptable appearance once healed (C).
250 mg antabuse saleAfter dividing, the common peroneal nerve then strikes obliquely throughout the distal thigh to travel on the lateral facet of the popliteal fossa. Close to its origin, a quantity of branches of the peroneal nerve go away to contribute to the formation of the sural nerve. Moving distally, the nerve then crosses the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle to attain the world just posterior to the fibular head. Once it curves over the posterior rim of the fibular head, it enters a tunnel fashioned by the 2 heads of the peroneus longus muscle and the fibular neck. The superficial portion of the nerve takes a relatively straight course to innervate the peroneus longus muscle and continues descending distally to innervate the peroneus brevis muscle. The nerve descends within the anterior compartment of the leg lateral to the tibialis anterior muscle. In the very distal portion of the leg, the nerve divides into medial and lateral terminal branches. The tibial nerve continues the road of the sciatic nerve after its bifurcation within the middle to distal third of the thigh. In the popliteal fossa, the tibial nerve turns into more superficial, first lying posterior and lateral to the popliteal vessels and then crossing obliquely to their medial side before moving into the leg. It travels distally within the leg between the gastrocnemius and the tibialis posterior muscle tissue. Finally, the nerve curves anteroinferiorly into the only of the foot behind the medial malleolus, deep to the flexor retinaculum and between the flexor hallucis longus and the flexor digitorum longus tendons. The nerve in the so-called tarsal tunnel ends at this degree as it divides into medial and lateral plantar nerves. The sural nerve, a cutaneous department of the tibialis nerve, arises on the center or lower facet of the popliteal fossa. After intubation and induction of general endotracheal anesthesia in the patient on a stretcher, the patient is placed on the operating table within the prone place on stomach bolsters. After the pores and skin is incised, the inferior margin of the gluteus maximus muscle is located. A cuff of muscle each medially and laterally have to be left for reattachment at the completion of the case. Exposure of the sciatic nerve extra proximal to the sciatic notch requires an stomach extraperitoneal method. The patient is positioned on the working desk in the prone position on stomach bolsters. The biceps femoris tendon can normally be palpated on the lateral side of the popliteal fossa and also wants to be marked. The pores and skin incision is laid out so that the proximal finish is simply superior to the popliteal fossa. In the mediolateral direction, it lies halfway between the biceps femoris tendon and the midline of the fossa. Care should be taken in making the skin incision, significantly across the fibular head, because the nerve is surprisingly superficial. Dissection should proceed to totally expose and establish both the superficial and deep branches of the nerve. The tibial nerve on the stage of the popliteal fossa is explored with the affected person within the inclined place. After intubation and induction of basic endotracheal anesthesia of the patient, usually on a stretcher, the patient is positioned on the working table on abdominal bolsters. The incision begins at the midline and extends distally to run obliquely throughout the popliteal fossa. It then continues laterally across the fossa and down the leg simply medial to the midline. Once the pores and skin and subcutaneous tissue are divided, the tibial nerve may be positioned within the midline in close approximation to the popliteal artery and vein. Much beyond the popliteal fossa, the nerve is difficult to expose, and a medial leg incision is necessary. The affected person is positioned within the supine place with a bolster beneath the contralateral buttock. The incision runs in a curvilinear method, in a radius approximately 2 to 3 cm around the posterior aspect of the medial malleolus. The incision also wants to lengthen no much less than 5 cm proximal to the malleolus up into the leg and 5 cm distal to the malleolus out onto the foot, paralleling the medial border of the plantar foot pad. The skin is incised, and after a small quantity of dissection, the tendons that course through the tunnel are immediately apparent. Just posterior to these tendons, the nerve, the posterior tibial artery, and the vein are situated. The artery and vein are often intertwined with the nerve at this level, which makes the dissection tougher. As the nerve is traced distally, further sectioning of the flexor retinaculum reveals the nerve dividing into medial and lateral plantar nerves and a calcaneal branch. The proximal belly of the abductor hallucis muscle could overlie the area the place the nerve divides. The belly of the muscle have to be partially sectioned to visualize this final portion of the nerve. It is somewhat awkward to perform in this position, significantly as the nerve is traced more proximally, however it might be accomplished. An incision is laid out two fingerbreadths posterior and two fingerbreadths superior to the lateral malleolus. If sural nerve publicity is required for operations that are performed with the patient inclined. The nerve and the muscle tendon are fairly superficial, and care must be exercised accordingly in making the incision. Care should be taken not to disrupt the lesser saphenous vein that travels with the nerve. If the nerve is traced proximally, it may be followed, accompanied by the lesser saphenous vein, until its disappearance beneath the two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle. Positioning for publicity of the sural nerve most often depends on the explanation for operation. The brachial plexus of nerves in man, the variations in its formation and its branches. Exploration of selected brachial plexus lesions by the posterior subscapular method. Persing random and axial flaps (based on a certain blood supply) safely and creatively to cowl a number of reconstructive issues. Any surgical incision ought to take into account esthetics in addition to therapeutic potential.
Leaves of Tomorrow (Ashitaba). Antabuse. - Acid reflux, peptic ulcers, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, gout, constipation, allergies, cancer, smallpox, food poisoning, and other conditions.
- How does Ashitaba work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Ashitaba.
- What is Ashitaba?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97078
Purchase antabuse 250mg otcThe coronal T1-weighted postcontrast picture (A) shows a solidly enhancing lesion infiltrating the corpus callosum, and the axial T1-weighted postcontrast picture (B) shows a faintly rim-enhancing lesion in the right frontal lobe. However, cases must be approached individually and be based mostly on an understanding of risk-benefit ratios in this inhabitants. These categories usually coexist in a given affected person and complicate diagnosis and therapy. For example, peripheral neuropathy may be attributable to the virus itself, by opportunistic infections, or by antiretroviral therapies. These problems embody lots of the problems whose analysis and remedy are more elusive, as outlined in Table 41-1. Motor slowing is normally evident, generally coincident with however often after the onset of cognitive decline. The ventricles and sulci are markedly prominent, indicating vital volume loss for a affected person of this age, but with minimal white matter signal abnormality. Specifically, proof for extra widespread infection of astrocytes and even of neurons may be discovered. The characteristic lesion in adults consists of vacuolar adjustments, predominantly within the lateral and posterior columns of the thoracic cord, although any degree could additionally be affected. Less widespread causes embrace those associated with malignancies, especially lymphoma and myeloma. Affected patients complain of numbness and burning sensation within the ft, which are exquisitely sensitive to contact. Distal reflexes are diminished in relation to proximal reflexes in a symmetrical method. Electrical studies reveal reduced nerve conduction velocities or amplitudes, or both, together with proof of denervation and reinnervation distally. Later in the middle of the disease, opportunistic infections could cause radiculopathies and mononeuritis multiplex. Treatment of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy includes identifying and correcting any comorbid nutritional or infectious elements, in addition to the usage of many medications, including analgesics of all lessons, anticonvulsants, anesthetic agents, and select antidepressants. Furthermore, several processes might coexist and thus complicate analysis and therapy. They trigger a constellation of neurological symptoms and findings that could be very tough to differentiate from one another, from lymphoma, and from tuberculosis. Reactivation occurs as a consequence of impaired cellular immunity and sometimes causes encephalitis with out important meningeal involvement. Multiple lesions can develop subacutely within the brain and cause location-dependent symptoms. The heart of the lesion may be hypointense on diffusion-weighted imaging, with the encircling edema being hyperintense. Although the lesions in lymphoma could be nodular and ring enhancing, a homogeneous pattern of enhancement is more common. Small parenchymal hemorrhages are frequent in toxoplasmosis and infrequent in lymphoma. Toxoplasmosis often responds quickly to remedy with pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine. Radiologic improvement is often apparent within 2 to 4 weeks, but in uncommon circumstances, sufferers might take up to 6 months to reply. Serum creatine kinase levels are regularly elevated, and electrical studies present basic myopathic modifications. T2-weighted and T1-weighted postcontrast pictures of the cerebral hemispheres (A and B) and the cerebellum (C and D) present quite a few edematous enhancing lesions. Toxoplasma lesions could be present in any location, they may be single or a quantity of, and they may exhibit any imaging structure from stable enhancing to ring enhancing, or a combination of each. The traditional look for toxoplasmosis is a ring-enhancing lesion with an eccentric enhancing nodule (arrow in B). In cases of failed analysis or failed response to empirical treatment of presumed toxoplasmosis, the neurosurgeon could need to carry out a biopsy. Biopsy specimens of toxoplasmotic tissue are sometimes necrotic, and when histopathologic evaluation fails to reveal organisms, other means of creating the analysis are needed,43,forty four including isolation of energetic T. In the event of suspected recurrence or progression due to drug resistance, repeat biopsy could also be warranted. The organism is present in bird excrement and infects people through inhalation, though overt pulmonary an infection and pneumonia are rare. Cranial neuropathies are widespread because of the predilection for meningeal involvement on the base of the brain. Male patient, 35 years old, who presented with seizures and no prior medical historical past. Coronal T2-weighted picture (A) and T1-weighted postcontrast image (B) reveal a single enhancing lesion in the posterior proper temporal lobe, which induced important edema. Note the looks of ring enhancement with an eccentric enhancing nodule (in B), which is classic for toxoplasmosis. Axial T2-weighted image (A) and T1-weighted postcontrast image (B) present a single small, enhancing lesion within the left corona radiata with moderate associated edema. Cryptococcal infection of the mind can take numerous forms, together with basilar meningitis, miliary parenchymal nodules, or, as in this case, a single parenchymal nodule. Because of its tendency to infiltrate the mind through the perivascular spaces, cryptococcal an infection can also cause dilation of the perivascular areas with or without enhancement: the so-called gelatinous pseudocyst presentation. Direct involvement of the brain parenchyma, when present, may be either focal or diffuse, and symptoms and signs range based on the area or areas affected. Sputum culture is unreliable due to fungi colonizing the upper respiratory tract. Male affected person, 37 years old and immunosuppressed, in whom cryptococcal meningitis was diagnosed by way of serologic testing of cerebrospinal fluid. T2-weighted axial photographs at barely different ranges (A and B) show bilateral lesions in the basal ganglia (arrows). Positive results of serum cryptococcal antigen testing by latex agglutination may also help support the diagnosis. These gelatinous dilations of the perivascular spaces are described as "cleaning soap bubbles. Treatment usually consists of fluconazole or amphotericin B (or considered one of its lipid derivatives). The majority of sufferers respond to treatment, however, as with toxoplasmosis, the relapse price is excessive. Aspergillus species are septate hyaline molds found in vegetation and soil that trigger extreme sinopulmonary infections in immunocompromised hosts. Aspergillus an infection could cause diffuse cerebritis, focal abscesses, or meningitis.
Generic 250 mg antabuse with visaStereotactic radiosurgery toxicity in the remedy of intracanalicular acoustic neuromas: the Seattle Northwest Gamma Knife experience. Long-term outcomes after meningioma radiosurgery: doctor and patient perspective. Surgery and radiotherapy in contrast with Gamma Knife radiosurgery within the remedy of solitary cerebral metastases of small diameter. Stereotactic radiosurgery for metastatic mind tumors: a comprehensive evaluate of problems. Radiographic findings and morbidity in sufferers treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Gamma knife radiosurgery for therapy of trigeminal neuralgia: idiopathic and tumor related. Magnetic resonance imaging analysis following intervertebral disk surgery, surgical decompression, intervertebral bony fusion, and spinal instrumentation: early complications of high-dose methylprednisolone sodium succinate remedy in the follow-up of acute cervical spinal twine harm. Postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leakage after lumbar backbone operations: conservative remedy. Prevention of subdural fluid collections following transcortical intraventricular and/or para-ventricular procedures by using fibrin adhesive. Effectiveness of fibrin glue for preventing postoperative extradural fluid leakage. Complications of posterior lumbar interbody fusion when using a titanium threaded cage device. The causes of failure of lumbar transpedicular spinal instrumentation and fusion: a potential research. Complications of anterior approaches to the thoracolumbar spine: emphasis on Kaneda instrumentation. Postoperative neurological deficits in segmental spinal instrumentation: a examine using spinal wire monitoring. Management of symptomatic lumbar pseudarthrosis with anteroposterior fusion: a functional and radiographic end result examine. Posterolateral lumbar and lumbosacral fusion with and with out pedicle screw inner fixation. Comparison of anterior and posterior instrumentation for correction of adolescent thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. The position of anterior lumbar interbody allograft bone dowel fusion as an adjunct to posterior segmental lumbar fixation. Posterior plates in the administration of cervical instability: long-term ends in forty four patients. Internal fixation in lumbosacral backbone fusion: a biomechanical and clinical study. Management of pseudarthrosis after arthrodesis of the spine for idiopathic scoliosis. Factors predicting postoperative problems following spinal fusions in youngsters with cerebral palsy. Efficacy of pedicle screw fixation within the remedy of spinal instability and failed again surgery: a 5-year review. Short phase posterior instrumentation, discount and fusion of unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures-a evaluate of 26 instances. Does anterior plating preserve cervical lordosis versus typical fusion strategies The position of acute decompression and restoration of spinal alignment within the prevention of post-traumatic syringomyelia: case report and evaluate of recent literature. Intraoperative ultrasound for immediate analysis of anterior cervical decompression and discectomy. Initial expertise with intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging in backbone surgery. A new strategy to computer-aided backbone surgery: fluoroscopy-based surgical navigation. Frameless stereotactic guided neurosurgery: medical expertise with an infrared primarily based pointer gadget navigation system. Improving accuracy and lowering errors in spinal surgery-a new method for thoracolumbar-level localization utilizing computer-assisted image steering. Placement of C2 laminar screws utilizing three-dimensional fluoroscopy-based image steering. A comparability of two methods in image-guided thoracic pedicle screw placement: a retrospective study of 37 sufferers and 277 pedicle screws. Miniature robotic steerage for backbone surgery-introduction of a novel system and analysis of challenges encountered during the medical improvement part at two spine centres. Significantly improved lumbar arthroplasty placement utilizing picture guidance: technical observe. Traumatic spinal twine harm as a complication to ankylosing spondylitis: an prolonged report. Spinal twine damage occurring in sufferers with ankylosing spondylitis: a multicenter examine. Fractures of the spine in ankylosing spondylitis: analysis, remedy, and issues. Management of cervical spinal cord harm in ankylosing spondylitis: the intervertebral disc as a reason for twine compression. Spinal twine damage, spinal fracture, and spinal stenosis in ankylosing spondylitis. The stabilizing effects of different orthoses within the intact and unstable higher cervical spine: a cadaver examine. Acute pulmonary edema following elimination of a spinal orthosis: an uncommon complication of a halo vest. The impact of torque stress on halo pin complication rates: a randomized prospective examine. Halo pin intracranial penetration and epidural abscess in a patient with a earlier cranioplasty: case report and evaluation of the literature. Clinical, radiographic, and kinematic results from an adjustable four-pad halo vest. Oropharyngeal morbidity following transoral approaches to the upper cervical spine. Odontoid upward migration in rheumatoid arthritis: an analysis of 45 sufferers with "cranial settling. Recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy after anterior cervical backbone surgery: the impression of endotracheal tube cuff deflation, reinflation, and strain adjustment. Intraoperative monitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve during revision thyroid surgical procedure.

Purchase cheapest antabuseThe prognosis should be suspected in these with typical pores and skin lesions or lymphadenopathy. His preliminary magnetic resonance imaging scans show a combined hyperintense and hypointense lesion (axial T2-weighted picture; A) with at least partial enhancement (axial T1-weighted postcontrast image; B) in the best paracentral lobule. An empirical trial of antitoxoplasmosis therapy was initiated, however after 1 month, follow-up scans confirmed important growth of the lesion (C and D). The prognosis itself (usually by stereotactic biopsy) has high specificity in most cases. Worldwide, toxoplasmosis accounts for almost all of those lesions (see earlier discussion). Nevertheless, empirical treatment of those situations often precedes attempts at biopsy in many cases. Thus many authorities advocate using empirical antimicrobial therapy for a defined period at the side of close medical statement for indicators of either improvement or deterioration. The majority of sufferers with cerebral toxoplasmosis show signs of clinical enchancment inside three days of therapy, and improvement on neuroimaging follows inside 7 to 10 days. Therefore, if this strategy is adopted, careful medical assessment should be maintained, and biopsy should be performed in any individual with early deterioration after the initiation of empirical therapy of presumed infectious illness. In immunosuppressed sufferers, lymphoma can manifest as a ring-enhancing lesion with cystic or hemorrhagic parts, but a solidly enhancing lesion is still the extra frequent appearance. Postcontrast axial computed tomographic image (A) demonstrates a quantity of giant parotid cysts (asterisks). An image directed barely extra cranially (B) reveals smaller parotid cysts along with a quantity of small adenoidal cysts (arrows). They occur most commonly in the parotid glands, and infrequently if ever happen within the other salivary glands because solely the parotid glands comprise intrinsic lymphoid tissue. Axial T2-weighted picture (A) shows very extensive, confluent sign abnormality in the white matter of the left cerebral hemisphere and, to a lesser degree, of the proper hemisphere. It is believed to mirror an exceptionally vigorous response of the newly reconstituting immune system to a preexisting infectious agent. Some authors have advised using steroids to dampen the immune response, notably if important cerebral edema or a mass impact is current. The clinician should contemplate the risk of multifactorial causes, many of which have related scientific and radiographic options. We have attempted to avoid dogmatic paradigms and schemata in addressing affected person administration as a end result of practice patterns are evolving and range considerably between developed and developing nations. Acknowledgments the authors are grateful to Koen van Besein, whose contributions had been essential to an earlier version of this chapter. Immune reconstitution associated with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in human immunodeficiency virus: a case discussion and evaluation of the literature. Declining morbidity and mortality amongst sufferers with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. Monocyte/macrophage trafficking in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome encephalitis: classes from human and nonhuman primate studies. Toxoplasmosis with early intracerebral hemorrhage in a patient with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Use of the serum reactivity against Toxoplasma gondii excreted-secreted antigens in cerebral toxoplasmosis diagnosis in human immunodeficiency virus�infected patients. Diagnosis of cerebral toxoplasmosis by detection of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites in cerebrospinal fluid. Successful medical treatment of multiple cryptococcomas: report of a case and literature review. Infections with Cryptococcus neoformans in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Evaluation of typical & serological methods for rapid analysis of cryptococcosis. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus an infection. Nontuberculous mycobacterial an infection of a metastatic brain neoplasm in an immunocompromised affected person. Clinical characteristics and comparability with cryptococcal meningitis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Tuberculous meningitis in sufferers contaminated with the human immunodeficiency virus. Dexamethasone for the therapy of tuberculous meningitis in adolescents and adults. Predictive elements for prolonged survival in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome� related progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Atypical transverse myelitis because of cytomegalovirus in an immunocompetent patient. Comparison of three nucleic acid amplification assays of cerebrospinal fluid for prognosis of cytomegalovirus encephalitis. Alteration within the natural history of neurosyphilis by concurrent an infection with the human immunodeficiency virus. Bartonella (Rochalimaea) antibodies, dementia, and cat possession among males contaminated with human immunodeficiency virus. Rapid polymerase chain reaction�based confirmation of cat scratch disease and Bartonella henselae infection. Additional experience with empiric radiotherapy for presumed human immunodeficiency virus�associated main central nervous system lymphoma. Primary lymphoma of brain: results of management of a contemporary cohort with radiation remedy. The therapy of primary central nervous system lymphoma in 122 immunocompetent sufferers: a population-based research of successively handled cohorts from the British Colombia Cancer Agency. High incidence of occult leptomeningeal disease detected by flow cytometry in newly diagnosed aggressive B-cell lymphomas in danger for central nervous system involvement: the position of circulate cytometry versus cytology. Central nervous system leiomyosarcoma in sufferers with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Multicentric intracranial smooth-muscle tumor in a woman with human immunodeficiency virus. Sensory neuropathy in human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients: protease inhibitor�mediated neurotoxicity. Malaria Plasmodium infections have a complex biologic cycle during which humans are contaminated via the skin throughout a blood meal by a female Anopheles mosquito. Fever is the initial grievance, followed by progressive somnolence associated with seizures, extensor posturing, and disconjugate gaze.
Cheap antabuse 500 mg with mastercardA Cobb elevator is used to expose the ipsilateral pedicle subperiosteally and to push the nerve root away dorsally without separating the foundation from the surrounding gentle tissue. The inferior margin of the pedicle is recognized with a nerve hook, and the pedicle is transected with a punch, which could be facilitated by thinning the pedicle with a high-speed bur beforehand. Removal of the dorsocranial section of the vertebral body with the bottom of the pedicle exposes the posterior margin fragment and brings the dura into view. The compressing fragment can now be lifted off the dura beneath direct view, mobilized within the path of the partial corpectomy, and resected. A nerve hook is used underneath image intensifier management to document the completeness of the posterior margin fragment resection in each planes. In cases with posterior wall resection, an expandable titanium cage is used as a vertebral physique replacement because of its larger main stability and the decrease risk of dislocation. The operation concludes with the ventral instrumentation and suturing of the diaphragm attachment. Removal of Protruded Herniated Disk: Endoscopic Treatment of Degenerative Disk Disease Only 0. Depending on the localization and enlargement of herniation-medial, mediolateral, intraforaminal, or extraforaminal-typical signs of thoracic disk herniation can be described. The spectrum of accidents to the spinal canal, medullary cone, and cauda equina ranges from simple contusion to complete tearing of the neural buildings. Thus the indications for anterior decompression are present when significant narrowing and a neurological deficit remain after main dorsal reduction and stabilization. OperativeTreatmentOptions the following surgical approaches22 are used to fit the wanted stage and herniation web site: � Transthoracic approach, open or endoscopic (T4-T11 stage, central disk herniation, with or without calcification) � Lateral extracavitary method (T6-T12 degree, centrolateral disk herniation)23 OperativeTechnique Completion of the partial corpectomy and adjacent diskectomies is really helpful earlier than the canal decompression. SpecialAnatomicConsiderations the difference between the thoracic backbone and the cervical and lumbar backbone is the presence of rib-attached vertebrae. Except for the primary thoracic vertebra, each rib articulates with the costovertebral joint through a cranial and a caudal half onto the neighboring vertebral our bodies. Because of that anatomic state of affairs, the rib head covers the dorsal disk house and the ipsilateral pedicle. The nerve root and the outgoing segmental vessels kind a bundle next to the rib head caudally, driving in a bone groove alongside the caudal rib ventrally. Therefore, the fluoroscopic visible again wall is created by summation impact; the anatomic concave again wall is ventral to that line. The aspect for the approach has to be dictated primarily by the localization of the disk herniation, signs, and the adjoining nice vessels. Verification of the level of disease could be troublesome earlier than the main process is began. Several methods are really helpful to make certain that the proper intervertebral disk house is addressed. Dickman and colleagues12 beneficial a preoperative radiograph of the chest to localize the extent. After the endoscopic process has began, it is suggested that the ribs be counted with use of the C-arm, starting caudally at the 12th rib. In sufferers with an irregular number of ribs, close consideration will prevent misidentification of the spinal stage. Radiographs showing dorsal discount and stabilization by internal fixator to obtain oblique decompression by ligamentotaxis. The tissue-preserving thoracoscopic approach6,12,25 is useful for higher numbers of indications, leaving centrolateral and lateral disk herniations to be approached posterolaterally. The thoracoscopic approach and operative approach are described here (Video 27-13). Radiographs displaying thoracoscopic reconstruction of the anterior column with anterior decompression. Calcified herniated disk on the T9-T10 stage with extreme narrowing of the spinal canal and twine in a 54-year-old lady, inflicting myelopathy and beltlike back pain. The affected section is marked on the best chest wall before the endoscopic procedure is started. The working portal shall be placed instantly above the pathologic process; the 30-degree endoscope might be inserted from below. A block-shaped defect is then created within the adjacent vertebral our bodies for removing of sentimental and calcified disk materials away from the dura and into the defect. Afterward, the rib head, which normally matches into the defect, is used for a monosegmental fusion procedure to be completed by ventral instrumentation. TechnicalandOperativeDetails A lateral fluoroscopic picture is obtained to decide the extent of illness and the position of the four portals. After the strategy has been made and all portals are correctly positioned, the spine is uncovered by retraction of the lung with the fan-shaped retractor. Mobilization of the rib head for entry to the T9-T10 intervertebral disk and the pedicle of T10. Partial corpectomy of T9 and T10 with a high-speed bur to create a defect within the vertebral our bodies in entrance. The procedure consists of partial removal of the disk, combined with a roughly extended bone defect at the adjacent vertebral our bodies; distinct instability thus could be anticipated. After trap-door incision of the pleura over the identified disk area and the adjacent one, the segmental vessels of no much less than the decrease adjoining vertebra are prepared, ligated with clips, and transected. If mobilization of the aorta is required, the segmental vessels are ligated and dissected at multiple levels. The capsular and ligamentous buildings of the rib head are reduce with a Cobb elevator, and the rib head is mobilized. The pleura is opened alongside the course of the proximal rib, and the proximal 2 cm of the rib is resected. A well-defined, block-shaped central defect involving the upper and lower thirds of the adjacent vertebral our bodies is created. Once the bottom of the pedicle caudal to the intervertebral disk space is recognized, the thickness may be reduced with a diamond bur to weaken the pedicle and to facilitate the transection with Kerrison rongeurs. Under direct endoscopic view of the dura, the posterior wall is then dissected off the dura and punctiliously pushed into the corpectomy website or thinned out with a high-speed diamond bur. Complete decompression of the dural sac throughout the vertebral physique to the level of the contralateral pedicle is confirmed by direct endoscopic view and radiologically by fluoroscopy with use of a nerve hook in an anteroposterior projection. The corpectomy defect is reconstructed, with the rib head harvested at step one. After the pedicle of T10 has been dissected, the posterior vertebral wall, including the calcified herniated disk, is carefully dissected from the dura and pushed into the vertebral defect in front. We routinely carry out a monosegmental endoscopic anterior fixation with a constrained screw-plate system to achieve a stable bony fusion of the section. Resection of Metastatic Spinal Tumors in Thorax and Thoracolumbar Junction: Special Considerations Minimally invasive thoracoscopic surgical procedure in sufferers with metastatic disease plays a significant function in minimizing surgical morbidity and restoration time.

Discount 500 mg antabuse free shippingThe surgeon not only must understand the nerve anatomy but additionally must have the flexibility to correlate neural constructions with their goal muscular tissues and sensory distribution. In much of nerve surgery, the traditional anatomy is distorted-from trauma, tumor, or different disease-and the surgeon should perceive the normal anatomy earlier than continuing. A correctly deliberate incision and exposure permit the right identification of the very important buildings, as properly as room by which to carry out the needed tasks. Neurosurgery of the mind and spine entails working in small, confined areas, whereas peripheral nerve surgical procedure often allows the luxury of working in a extra open, extra exposed area. The surgeon ought to reap the benefits of this case and make the exposure beneficiant. Whenever potential, publicity of a nerve ought to include regular proximal and distal areas of the nerve to enable the surgeon to work from the traditional to the abnormal areas and back to the conventional area. The particular nerve or nerves to be operated on and the necessity of harvesting grafts will dictate much of the positioning for an operation. If intraoperative electromyographic monitoring of muscular tissues is used, the limb may be draped out of the sphere. If, however, muscle contraction must be noticed and no monitoring is used, the complete limb have to be both uncovered or coated with clear plastic drapes. In every case, the positioning and exposure must be arranged to suit the individual needs of the actual operation. More in-depth viewing of positioning for peripheral nerve surgery is on the market on Video 22-1 and on individual video clips that focus on every anatomic area. Upper Extremity See also the following video clips demonstrating correct positioning for the exposure of assorted nerves in the higher extremities: Video 22-2. The brachial plexus is formed by the ventral primary rami of spinal nerves C5 to T1. The patient is placed within the supine place with the arm abducted on an arm board. The sulcus between the biceps brachii and the triceps muscles is located, palpated, and traced proximally to the anterior axillary fold. The skin is then incised along the tracing, the interval between the biceps brachii and triceps is developed, and the brachial fascia incised. The incision begins 2 to three cm above the medial epicondyle over the medial intermuscular septum. The incision continues distally over the bicipital aponeurosis (lacertus fibrosus) in a delicate curve toward the midline of the forearm. The incision then strikes distally down the forearm, following the interval between the flexor digitorum superficialis and the brachioradialis muscular tissues. The incision is opened proximally, and the median nerve is located in the interval between the biceps brachii muscle and the medial intermuscular septum. The nerve is traced into the forearm, and the lacertus fibrosus (bicipital aponeurosis) crosses its path obliquely. The nerve then moves deep to the arch of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle, and this arch is surgically divided. The median nerve might then be traced to the wrist, the place it lies between the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor digitorum superficialis muscles. This patient had undergone previous radiation therapy to the anterior facet of the neck; therefore, a traditional strategy to the plexus was not possible. An extra bolster should be placed under the patient at the degree of the clavicle and higher sternum so that the anterior chest wall is lifted slightly off the operating desk. Kline and associates3 and Maniker4 offered additional details of this place and method. These approaches may be mixed for the complete exposure of the plexus or tailor-made to expose the specified space of the plexus. The supraclavicular portion of the strategy exposes the roots, trunks, and proximal portion of the divisions. In this place, the surgeon could transfer from the posterior facet of the patient to the anterior facet of the patient to reach the radial nerve distal to the spiral groove. The anatomy and surgical exposure of the median nerve within the wrist are coated in other chapters. The surgeon is most snug superior to the arm, simply lateral to the neck and head of the patient. The incision begins three to four cm proximal to the elbow flexion crease in the interval between the biceps brachii and brachioradialis muscular tissues. It crosses the elbow flexion crease obliquely and then curves down onto the forearm lateral to the biceps brachii tendon. The incision should reach the midline of the forearm four to 5 cm distal to the elbow flexion crease after which continue distally in the forearm just radial to the midline. The nerve could additionally be identified within the interval between the biceps brachii and brachioradialis muscular tissues simply proximal to the elbow flexion crease. The nerve is then traced down into the plane between the brachioradialis and extensor carpi radialis longus muscle tissue. The posterior interosseous nerve must be traced distally as it passes beneath a vascular leash of vessels, inferior to the arcade of Frohse, and into the supinator muscle. If the radial nerve needs to be uncovered only from the triangular interval (where it emerges into the posterior compartment of the arm) to the spiral groove, the affected person could also be positioned within the lateral decubitus, the inclined, or the supine position. I discover that the lateral decubitus place presents the most comfortable positioning for this exposure. If the nerve must be exposed on each side of the spiral groove, the posterior and anterior surfaces of the arm should be obtainable for publicity. In this case also, the affected person could also be positioned in the lateral decubitus, prone, or supine place. Retraction of the superficial muscle exposes the radial nerve and profunda brachii artery. The radial nerve might then be traced distally because it passes from the posterior compartment into the anterior compartment of the arm. The posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm could cross the operative field, and it should be identified and protected. Once the skin is retracted, the nerve could additionally be found throughout the cubital tunnel and traced each proximally and distally as needed. Lower Extremity See additionally the next video clips demonstrating proper positioning for the exposure of varied nerves in the lower extremities: Video 22-13. Tarsal Tunnel (Medial, Lateral Plantar, and Calcaneal Nerves) SciaticNerve Anatomy. Just caudad to this muscle, the nerve enters the buttock by way of the sciatic foramen. The nerve then strikes laterally in an oblique course beneath the gluteus maximus muscle towards the midline of the posterior facet of the leg. In nearly all of people, the nerve divides into tibial and common peroneal branches at the middle to distal third of the thigh. For instance, a coronal incision can be adapted as far posterior as potential, offering wonderful exposure, and can additionally be able to be properly hidden, even with a receding hairline. Closing a surgical incision entails contemplating the reconstructive ladder, typically used by plastic surgeons to reconstruct numerous tissue defects.
References - Szymanski KM, Whittam B, Kaefer M, et al: What about my daughteris future? Parental concerns when considering female genital restoration surgery in girls with congenital adrenal hyperplasia, J Pediatr Urol 14(5):417, e1n417. e5, 2018.
- Ismail M, Gomella LG: Transrectal prostate biopsy, Urol Clin North Am 40(4):457n472, 2013.
- DasGupta R, Fowler CJ: Urodynamic study of women in urinary retention treated with sacral neuromodulation, J Urol 171:1161n1164, 2004.
- Rappaport BA, Suresh S, Hertz S, et al: Anesthetic neurotoxicity?clinical implications of animal models, N Engl J Med 372:796-797, 2015.
|
|